US-China Carbon Consortium (USCCC)
Site Locations
The USCCC has site locations ranging across varying ecosystems in US and China. Read detailed descriptions about each individual site below or click these pins in the interactive Google Maps to see the details of each site. You can also download Google Earth .kmz file to explore sites in Google Earth Pro.
Download KMZ file
Download Google Earth Pro (free)
Aquatic Ecosystems

- Team: Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGLAS, CAS) | Quantitative Remote Sensing for Hydroclimatology (QRSH)
- PI: Dr. Yuanbo LIU
The Poyang Lake site was established on July 26, 2013 when an eddy covariance system was installed on the flux tower at a height of 38m on Sheshan Island in Poyang Lake, which is located in Jiangxi Province, China (29.83N,116.30E). The island is located in the center of the lake, and which has a remarkable seasonal variation and a stage change of 10m per year. The site belongs to the subtropical climate monsoon region with an annual mean air temperature of 17.1 °C, and annual precipitation of 1570 mm.

The Yunxiao Mariculture Pond site was established in Dec. 2019 when an open-path eddy covariance system was deployed on the flux tower at a height of ~ 5 m above mariculture ponds, located in Zhangjiang estuary, Yunxiao, Fujian, China (23.9314°N, 117.4084°E). Razor clam is the dominant farming species for these mariculture ponds. The climate in this region is subtropical marine monsoonal climate with a mean annual air temperature and precipitation of 21.2 ? and 1714.5 mm, respectively. For this site, carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor and energy fluxes were measured, and an array of meteorological and water quality parameters were also obtained.
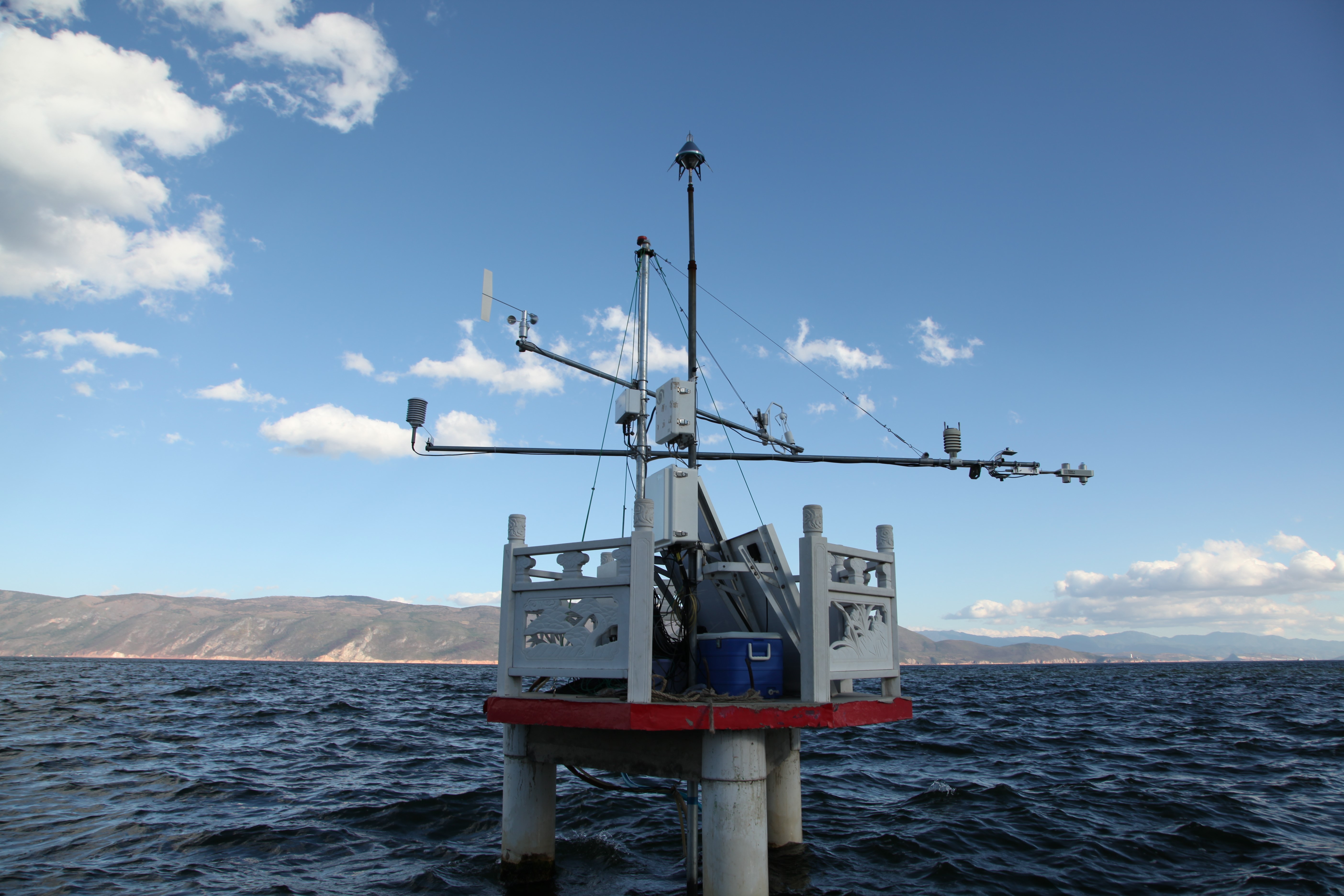

- Team: Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Erhai Lake (25°46' N, 100°10' E) is situated at the Dali Autonomous Prefecture of Yunnan Province in southwest China, 1972 m above sea level. This site was built in June 2011. The climate in Dali area is a mild subtropical highland climate. The lake was formed by the subsidence of a geological fault. The length of the lake is about 40 km from north to south and roughly 7-8 km from east to west. It covers an area of more than 250 km2, making it the second largest highland lake next to Dianchi lake and one of the seven biggest fresh water lakes in China. The maximum depth is 21.5 m at the middle of the lake. The lake is sandwiched between Cangshan Mountains in the west and Yuan Mountains in the east. It receives water from the Mimu River, the Luoshi River, the Yongan River and many small streams from the Cangshan Mountains, but it has only one outlet (Xier River) in the south used for irrigation during the dry season and eventually flows into the Lancang River. The lake is ice-free throughout the year. An open-path EC system was installed on a concrete platform to measure water vapor and CO2 fluxes over the lake.

- Team: Washington State University (Dr. Heping Liu)
The Ross Barnett Reservoir is located in central Mississippi (32°26'N, 90°02'W), USA, and has a surface area of about 134 km2 and water depths varying from 4 to 8 m. The reservoir is ice-free year round. A 5m tower (Climatronics Corp.) was installed in 2007 over a stationary wooden platform in the south center of the reservoir, with the mean water depth around the tower of about 5m and the distance from the tower to the shore ranging from 2 km to more than 14 km. An eddy covariance system at a height of 4m above the water surface is used to measure CO2 fluxes. The system consists of a three-dimensional sonic anemometer (model CSAT3, Campbell Scientific, Inc.) and an open path CO2/H2O infrared gas analyzer (IRGA; Model LI-7500, LI-COR, Inc.). Three-dimensional wind velocity components and sonic virtual temperature from the sonic anemometer and densities of carbon dioxide and water vapor from the IRGA are recorded by a datalogger (model CR5000, Campbell Scientific, Inc.) at a frequency of 10 Hz. Other microclimate variables are also measured as 30 min averages with 1 s readings, including net radiation (Rn) at 1.2m (model Q-7.1, Radiation and Energy Balance Systems, Campbell Scientific, Inc.), air temperature (Ta) and relative humidity (RH) (model HMP45C, Vaisala, Inc.) at 1.9, 3.0, 4.0, and 5.5 m, wind speeds (U) and wind direction (WD) (model 03001, RM Young, Inc.) at 5.5 m. The water skin temperature (Ts) is measured by an infrared temperature sensor (model IRR-P, Apogee, Inc.). Water temperatures at eight depths of 0.10, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, and 4.5mbelow the water surface are measured at 1 min interval and then integrated into 30 min mean values by eight water temperature probes (model 107-L, Campbell Scientific, Inc.), all tied to a buoy. Half-hourly precipitation totals are measured using an automated tipping-bucket rain gauge (model TE525, Texas Instruments, Inc.). All instruments are powered by six deep-cycle marine batteries that were charged by two solar panels (model SP65, 65 Watt Solar Panel, Campbell Scientific, Inc.).
Cropland Ecosystem

- Team: Michigan State University | Landscape Ecology and Ecosystem Science Lab (LEES Lab)
- PI: Dr. Jiquan Chen
The GLBRC scale-up fields are located at the KBS LTER sites of Michigan State University, in Southwest Michigan (42°24' N, 85°24' W, 288 masl). The region has a humid, temperate continental climate with mean annual air temperature of 9.9°C and precipitation 1027 mm. The soil is moderately to slightly acidic, well drained sandy loams. Before land use conversion to biofuel crops, three sites were managed under the USDAs CRP (Conservation Reserve Program) since 1987, and three other sites were under conventional row crop corn/soybean agricultural (AGR) rotation for several decades.
In 2009, all six sites were converted to no-till soybean. Starting from 2010, three of the former CRP and three of the former AGR lands were each planted with no-till continuous annual corn, and perennial switchgrass and mixed-prairie. One CRP site was maintained as a reference. Each site is equipped with eddy flux tower and ancillary meteorological instruments. The set-up and measurements at these sites provide a unique opportunity to study the sustainability of converting grass- and agricultural lands for grain and cellulosic biofuel production at the interface of social, economic and environmental issues.
- Team: Southwest University, China | Heihe Remote Sensing Experimental Research Station, Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences
- PI: Dr. Che Tao
Daman Superstation is a farmland flux observation station and is affiliated with the Heihe Remote Sensing Experimental Research Station, Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAREERI,CAS). It is located in the Daman irrigation farmland of Zhangye city, GanSu province and belongs to the administrative divisions of five-star village, Xiaoman town, Zhangye city.
There is a gradient meteorological tower of measuring 40 m high in the observation field. Flux observation is located in the tower. The observation coordinates are 100°22'20.2"E, 38°51'20.0" N, 1556 m, and the underlying surface of flux station is farmland and the main crop type is maize. The station represents seed maize type in the middle latitude hinterland of mainland, which belongs to the Zhangye Oasis in the middle basin of the Heihe River.

Nashville, Tennessee is located in the southeastern United States. While this region is in a temperate climate with deciduous forests, agricultural activities are intensive in the region as well. Crops such as corn, soybean, and cotton have been grown extensively. Grasslands and pastures are also common and cows and goats are raised by farmers. This eddy flux tower can be set in different ecosystems to monitor ecosystem exchanges of carbon, nitrogen and water fluxes.
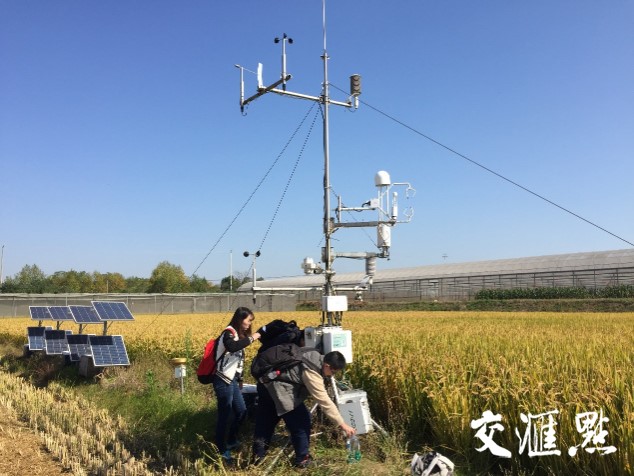

- Team: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology (NUIST) | International Center for Ecology, Meteorology, and Environment (IceMe)
- PI: Dr. Lu Hao
The Lishui Rice Paddy field is located at the Lishui Experiment Station of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences in Nanjing (31.6°N, 119.2°E, 38 masl). The local climate is controlled by the East Asia summer monsoon with mean annual air temperature of 15.4°C and precipitation 1116 mm. The underlying surface of flux station is farmland and the main crop type is rice paddy. The station is located in the Qinhuai River basin which represents a typical landscape of the lower Yangtze River Delta region that is characterized by its flat topography with natural river networks which are severely modified, and land use which is dominated by paddy rice fields, dotted with small irrigation ponds that have been converted from natural wetlands over thousands of years. The Lishui eddy flux research site was installed in 2016 to measure water, energy and carbon fluxes including CO2 and CH4 and ancillary meteorological variables. The set-up and measurements at this site provide a unique opportunity to study the environmental impacts of converting traditional rice paddy fields to urban use for better management of urbanizing watersheds in the rice paddy-dominated landscape. The research is funded by China Natural Science Foundation.

- Team: (1) The Meteorological Science Research Institute of Anhui Province, Yong Huang, hy121_2000@126.com; (2) Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Fangmin Zhang, fmin.zhang@nuist.edu.cn
- PI: Dr. Yong Huang and Dr. Fangmin Zhang
Shouxian National Climatological Observation (32°26'N,116°47'E) is one of the five pilot climate observatories set by China Meteorological Administration (CMA), and located in the Huaihe River basin (also located in transition zone of subtropical to warm temperate zone in East Asia), belong to the Huanghuai agro-ecological observation area of China Climate Observing System (CCOS). The observatory established in 1955, experienced three times move, and covering 200000 m2 at present, which located in prime cropland preservation area of rice-wheat rotation. As one of the eight stations in China which still keep manual weather observation, the observatory carry out long-term manual and automatic observations. Some of the observation projects carried out in the observatory are as follows: ? China-Japan cooperation "Huaihe River Basin Energy and Water Cycle Experiment and Research (HUBEX)", "Lower Atmosphere Flux and Precipitation Study (LAPS)" ? China-US cooperation "Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) Mobile Facility(AMF) "
Desert Ecosystems

- Team: Michigan State University | Landscape Ecology and Ecosystem Science Lab (LEES Lab)
- PI: Dr. Jiquan Chen
The Siziwang desert steppe region belongs to the mid-temperate zone and has a distinct continental climate. The long-term mean annual air temperature of the region is 6.7°C, with the highest monthly mean temperature in July (22.6°C) and the lowest in January (11.6°C, average of 1971–2000). The mean annual rainfall is 180 mm but varies from year to year with strong seasonal variability. The soil is a light-colored Chernozemic soil (Chinese System of Soil Classification 2001) and is equivalent to Cryolls (USDA Soil Classification System). The fetch for the ungrazed fenced steppe (Tower A, 41.786 73 N, 111.890 95 E), which was fenced in June 2004, was 500 m2 x 100 m2, and the free-grazed steppe (GS, 41.790 N, 111.897 E) was more than 500 m in all directions. Grazed (stocking rate: ~2 sheep unit ha-1 half yr-1) site was under collective sheep grazing for over 30 years, which represents a common grazing intensity for the region.
Forest Ecosystems
- Team: Chinese Academy of Forestry
- PI: Dr. Xudong Zhang 张旭东
The Anqing Poplar Plantation is ~260 ha area located on the floodplain in the middle reaches of Yangtze River, with coordinates 29°31'N, 112°51'E. This site is also in the subtropical region of China, with a long-term, mean annual temperature of 17.3°C and a mean annual precipitation of ~1400 mm. The soil was fluvo-aquic soil, too. This site is also surfed by seasonal inundated as Yueyang Poplar Plantation site, and had the similar understory vegetation composition. The poplar plantation was established in 1989 with different poplar clones of Populus dettoides, and was selective-cut in 2008, after that the flux measurement ceased.
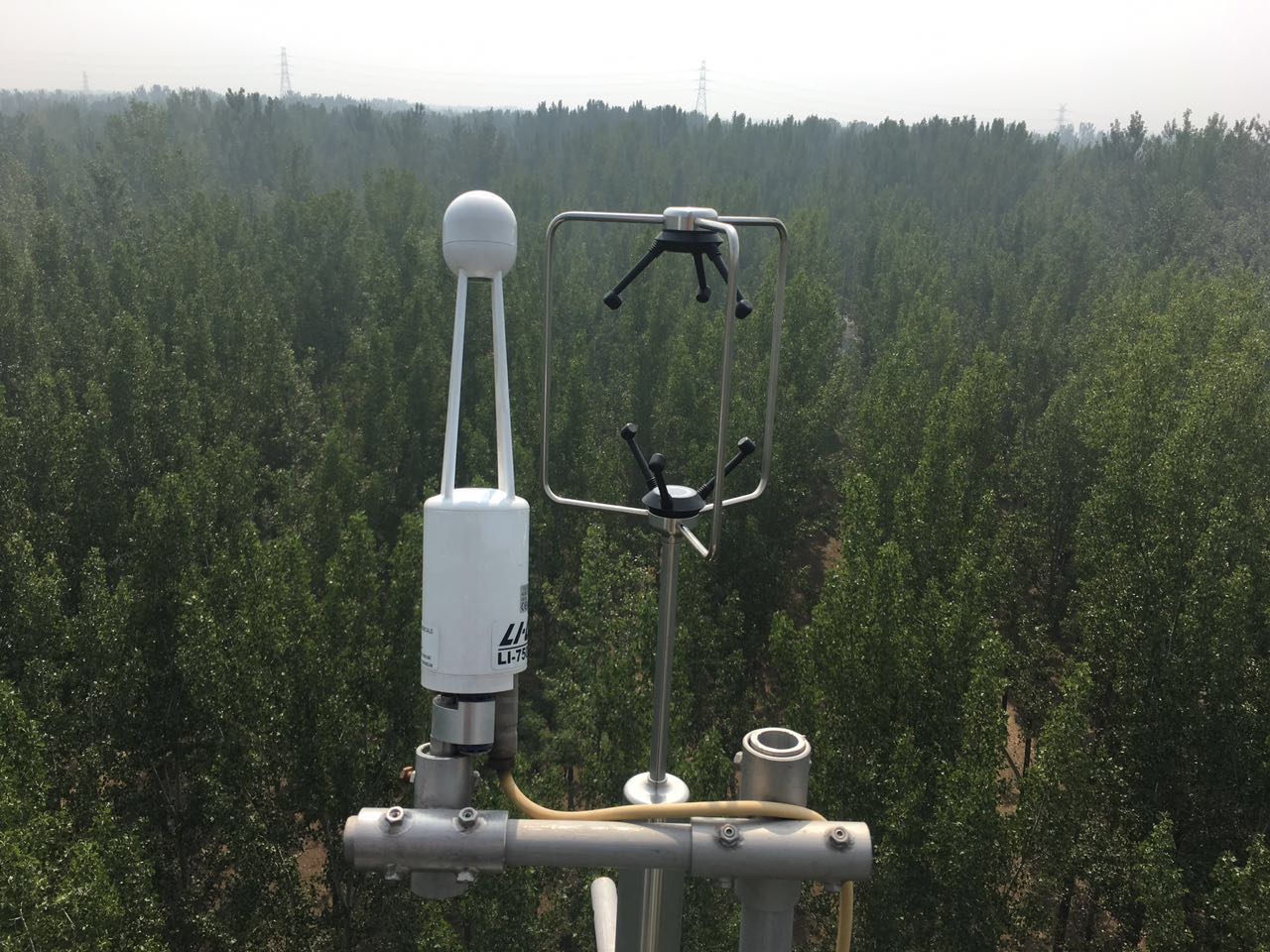

- Team: Beijing Forestry University
- PI: Dr. Zhiqiang Zhang & Dr. Hang Xu
This site is located in the Shunyi Forest Farm (116°42'41?E, 40°06'27?N, 29 m a.s.l.) in Beijing, China. The terrain is a fluvial plain of the Chaobai River with a stable groundwater level of around 2 m. The 178-ha forest consists of a 25-year-old plantation dominated by poplar (Populus euramericana cv.'74/76') in 2020, with a planting density of 4 m×3 m. By the end of 2020, the average height of the trees was 20.4 ± 1.6 m (mean ± SD) and the mean diameter at breast height (DBH) was 26.3 ± 1.5 cm. Understory shrubs mainly include Swida alba Opiz., Sorbaria sorbifolia, Forsythia suspense and Sabina vulgaris, and had been maintained at low densities since the initial establishment of the plantation. The study site is characterized by a warm temperate sub-humid continental monsoon climate, with a mean annual temperature of 11.5°C, a mean annual precipitation of 576 mm and a mean annual relative humidity (RH) of 50%. The soil type is classified as Entisol and the texture is sandy with a bulk density of 1.37 ± 0.04 g cm-3. The fine root mass (ca. 70%) is mainly distributed in the 20-50 cm soil layer (Xu et al. 2017, 2018, 2020).
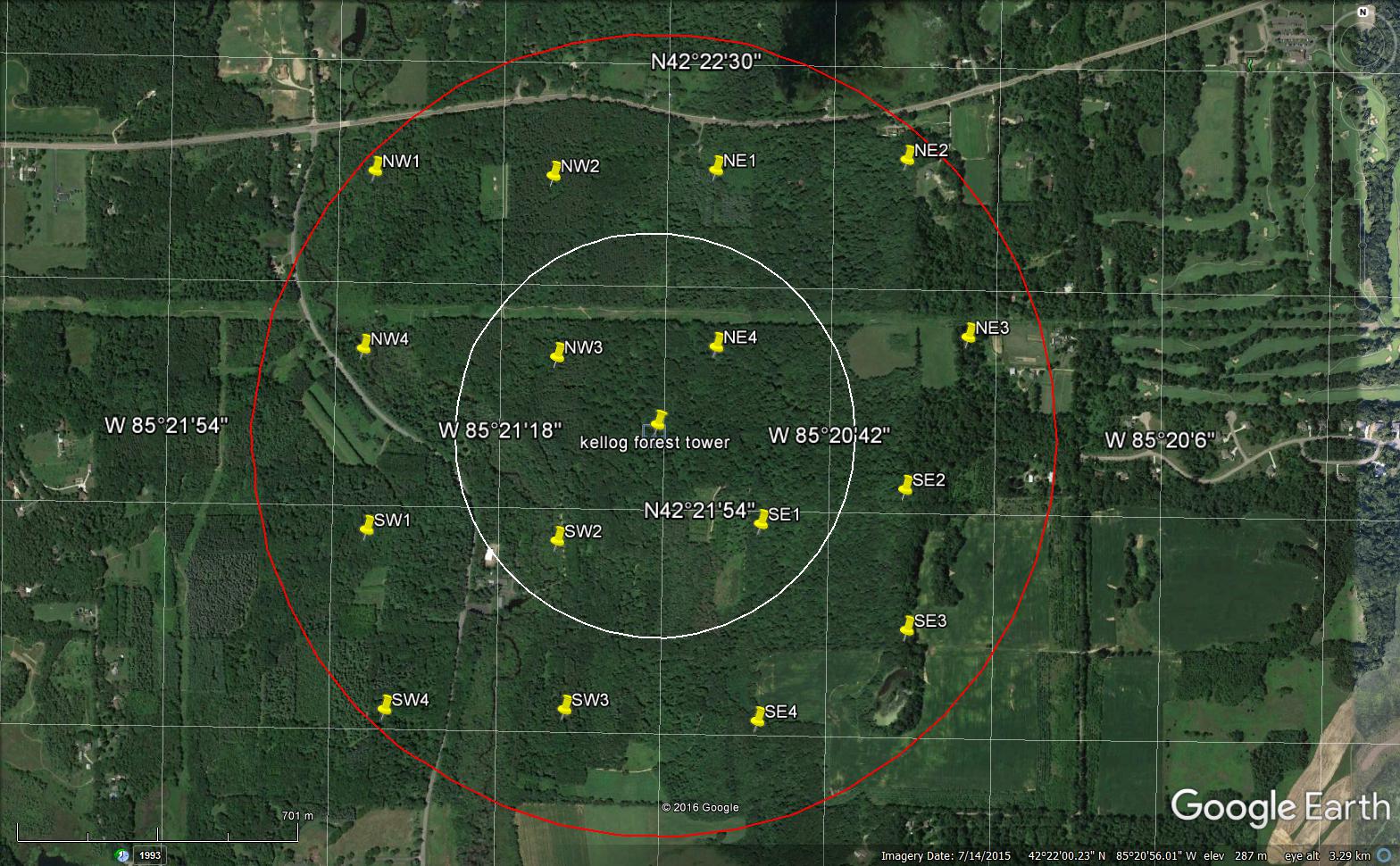
- Team: Michigan State University
- PI: Dr. Jiquan Chen
This forest tower is located at the Kellogg Experimental Forest in Southwest Michigan (42.366691, -85.353905) and is part of the Michigan State University watershed-scale flux sites along the Kalamazoo river in SW Michigan that seeks to answer the following questions: (1) What are the quantitative contributions of land cover change, specific management practices, and climate changes (means and extremes) to the social and physical C fluxes of managed ecosystems and landscapes? (2) What are the spatial and temporal changes of their contributions in managed agricultural-forest landscapes? (3) How will future land use changes (including alternative management practices) impact C sequestration in an upper, mid-latitude managed ecosystem? The forest stand Kellogg Experimental Forest was established on abandoned agricultural land and boasts 716 acres of mixed forest reaching canopy heights of ~30m. It has been managed by Michigan State University since 1932. The forest is dominated by a mix of maple, oak and pine, and hosts research plots for tree breeding and genetics, planting techniques and plantation establishment and management, as well as 16 FIA (i.e., forestry inventory analysis) inspired research plots. The forest is open to public use, including biking, hiking, equestrian activities, and cross-country skiing with several trails. Due to this mixed management and land use, the site was chosen to represent managed forests in the Kalamazoo River watershed.
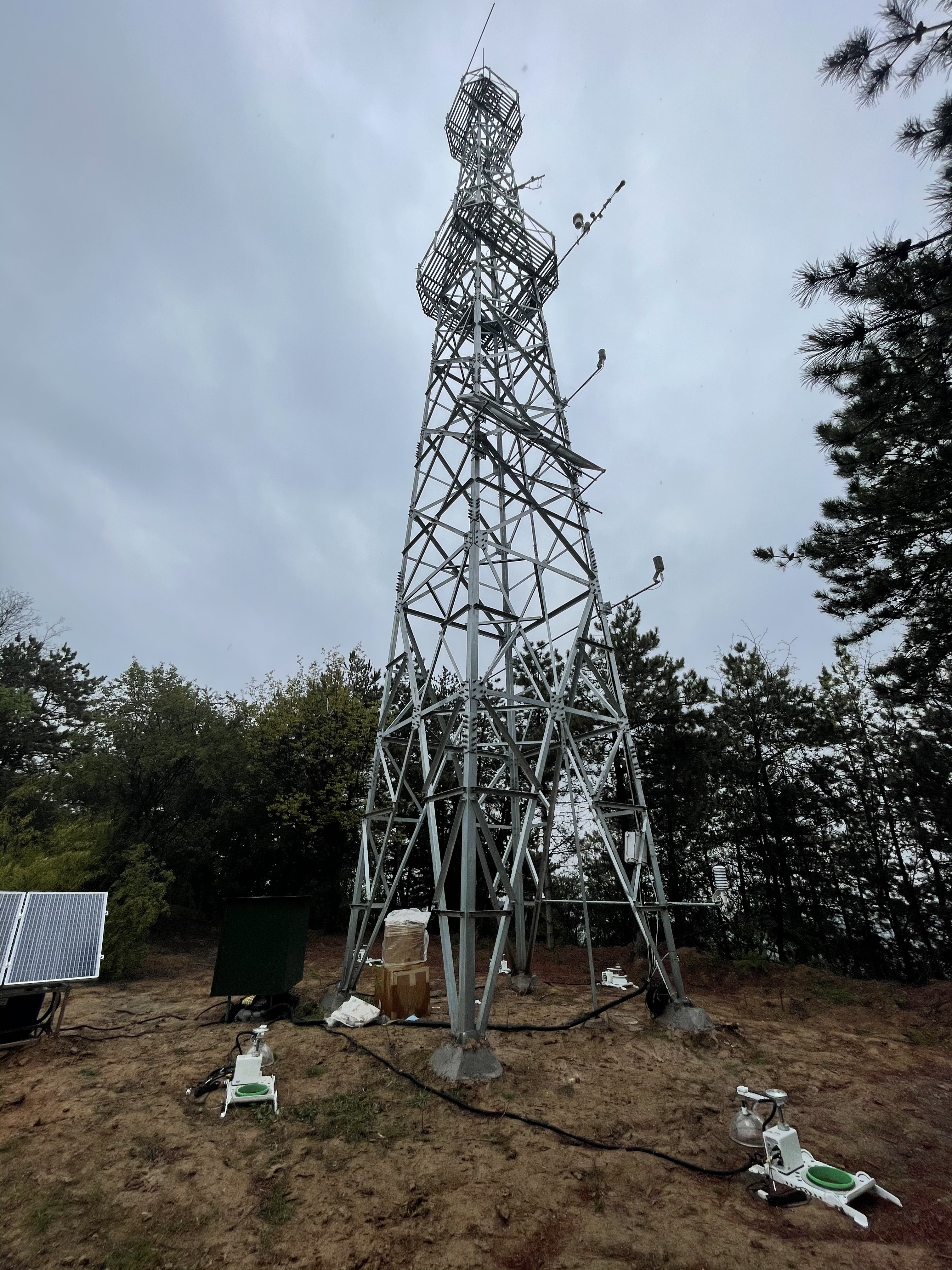

- Team: Beijing Forestry University
- PI: Dr. Zhiqiang Zhang & Dr. Hang Xu
This site is located in Jixian (110°43'27"E, 36°14'48"N, 1246 m a.s.l.), Shanxi Province on the Loess Plateau of China. The secondary mixed forest mainly consists of larch and oak trees without human management. The average age of the main tree species is about 30 years old, and the average height is 10 m in 2021. There are abundant types of understory vegetation, mainly including Vitex negundo Linn. var., Lespedeza bicolor Turcz., Rosa xanthina, Artemisia sacrorum and Carex callitrichos. The study site is characterized by a temperate continental monsoon climate, with a mean annual temperature of 10°C and a mean annual precipitation of 579 mm concentrated in June-August (70% of the whole year). The soil belongs to cinnamon soil, the parent material of loess.

- Team: Michigan State University | Landscape Ecology and Ecosystem Science Lab (LEES Lab)
- PI: Dr. Jiquan Chen
The Oak Openings Region is a 130 square mile (Moseley, 1928) area located in Lucas, Henry and Fulton Counties of Ohio, with coordinates 41.551807, -83.8502312. The region supports a mosaic of Great Lakes twig-rush wet meadow (wet prairie), Great Lakes swamp white oak - pin oak flatwoods, mesic sand prairie, Midwest sand barrens, black oak / lupine barrens (oak savanna), and black oak - white oak / blueberry forest (oak woodland) communities that developed on a series of post-glacial beach ridges and swales.
The region has a remarkable number of rare and endangered species including 145 plants that are currently listed as potentially threatened, threatened or endangered in Ohio. The area is severely fragmented and intermittent with agricultural lands, but represents the best-preserved remnant of Oak Openings habitat in Northwest Ohio and Southeastern Michigan and is one of the few landscape scale oak savanna/prairie complexes left in the Midwest.
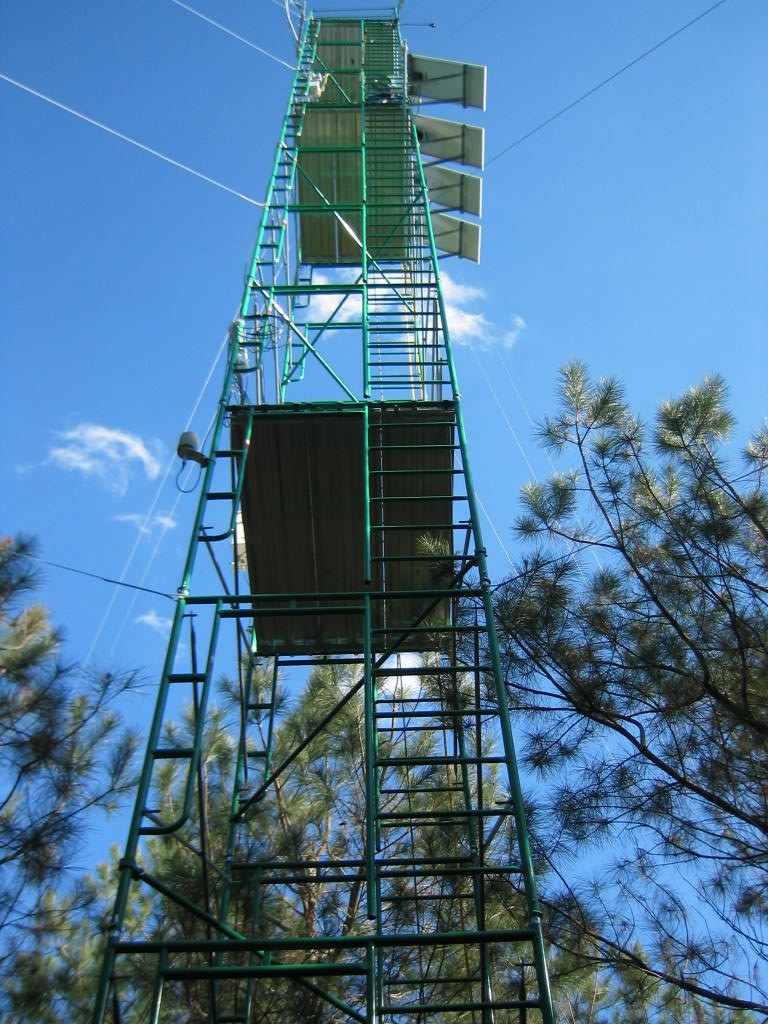

- Team: NCSU, TXAM, USFS
- PI: John King (NCSU), Asko Noormets (TXAM), Ge Sun (USFS), Steve McNulty (USFS)
These forested sites are on flat, poorly draining soils with shallow groundwater tables on the lower costal plain of North Carolina, eastern U.S. Company (Noormets et al., 2010; Sun et al., 2010; Aguilos et al., 2020, 2021a, 2021b). As part of the FLUXNET, the NC flux cluster sites are coded as US-NC3 (35.7990, -76.6560) , USNC1(35.8118, -76.7119 ), US-NC2 (35.8030, - 76.6685 ), and US-NC4 (35.788, -75.904) representing different ages of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) stands and a natural bottomland hardwood forested wetland (NC4) (>100 years old). The three loblolly pine plantations are managed by Weyerhaeuser Company. NC2 stand was recently cut in 2020 after monitoring for 15 years since 2005 when the plantation was 15 years old. During the 15 years, a thinning operation at the NC2 site occurred in 2009. The nearby tower (NC1) was built in 2005 after a harvesting operation and replanting of 1-year old pine seedlings. Measurement at NC3 (a new clear cut site) started in 2012. The pine stands at the managed plantation sites are drained with a network of parallel ditches, 90-130 cm deep on 90-m spacing, and more widely spaced roadside canals. Watershed yield (outflow) is monitored on the downstream end of the drainage network using a V-notch weir. Parallel ditches and roadside canals divide the flat landscape into a mosaic of regularly shaped fields and blocks of fields. NC4 is located in a protected wildlife refuge near the coastal NC.
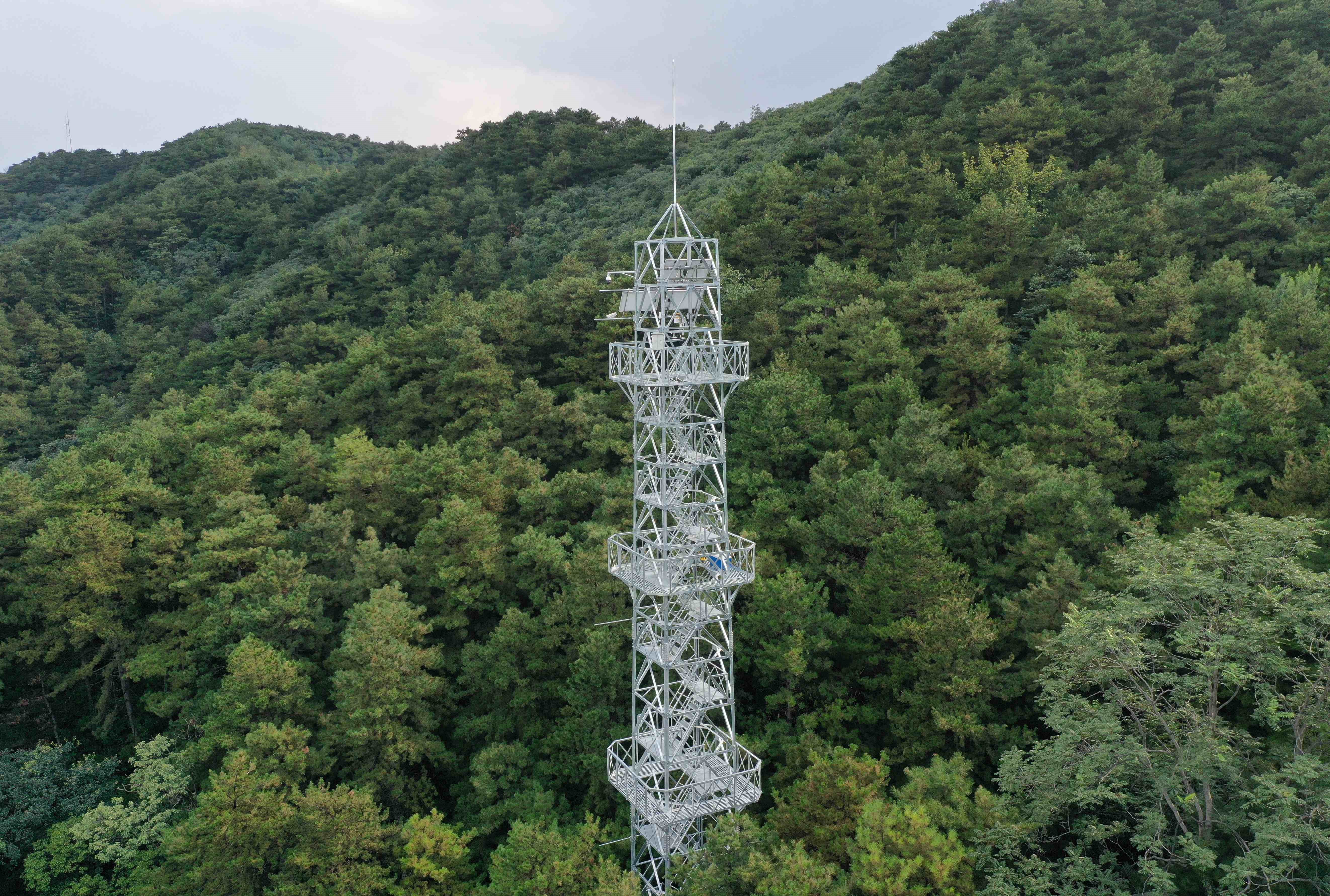

- Team: Beijing Forestry University | Beijing
- PI: Dr. Tianshan Zha, Dr. Peng Liu, Dr. Xin Jia
Miyun Chinese Pine Ecosystem Observation Station (MYP) is located in the west of the Miyun Reservoir, Miyun District, Beijing (40°29'52?N, 116°48'45?E, 1151 m a.s.l.), as a member of the Beijing Landscaping Ecosystem Observation Network (BJLEN). The site is characterized by a warm temperate monsoonal continental climate, with a mean annual temperature of 10.8 ?, a frost-free period of 260 days per year, and a mean annual precipitation of 500 mm. The vegetation type is evergreen coniferous forest dominated by Pinus tabulaeformis, which has a mean height of 8.2 m and a mean diameter at breast height (DBH) of 24.8 cm. The understory consists of Amygdalus davidiana and Vitex negundo. The soil is of the cinnamon type. Measurements at MYP include eddy-covariance fluxes (ecosystem carbon, water and energy exchange), environmental variables (air temperature and humidity, radiation, soil temperature and soil moisture, etc.), air quality variables (PM2.5, PM10, NOx, SO2, CO, O3 and negative oxygen ions) and sap flow rates (transpiration). Measurements at MYP started in January, 2021.
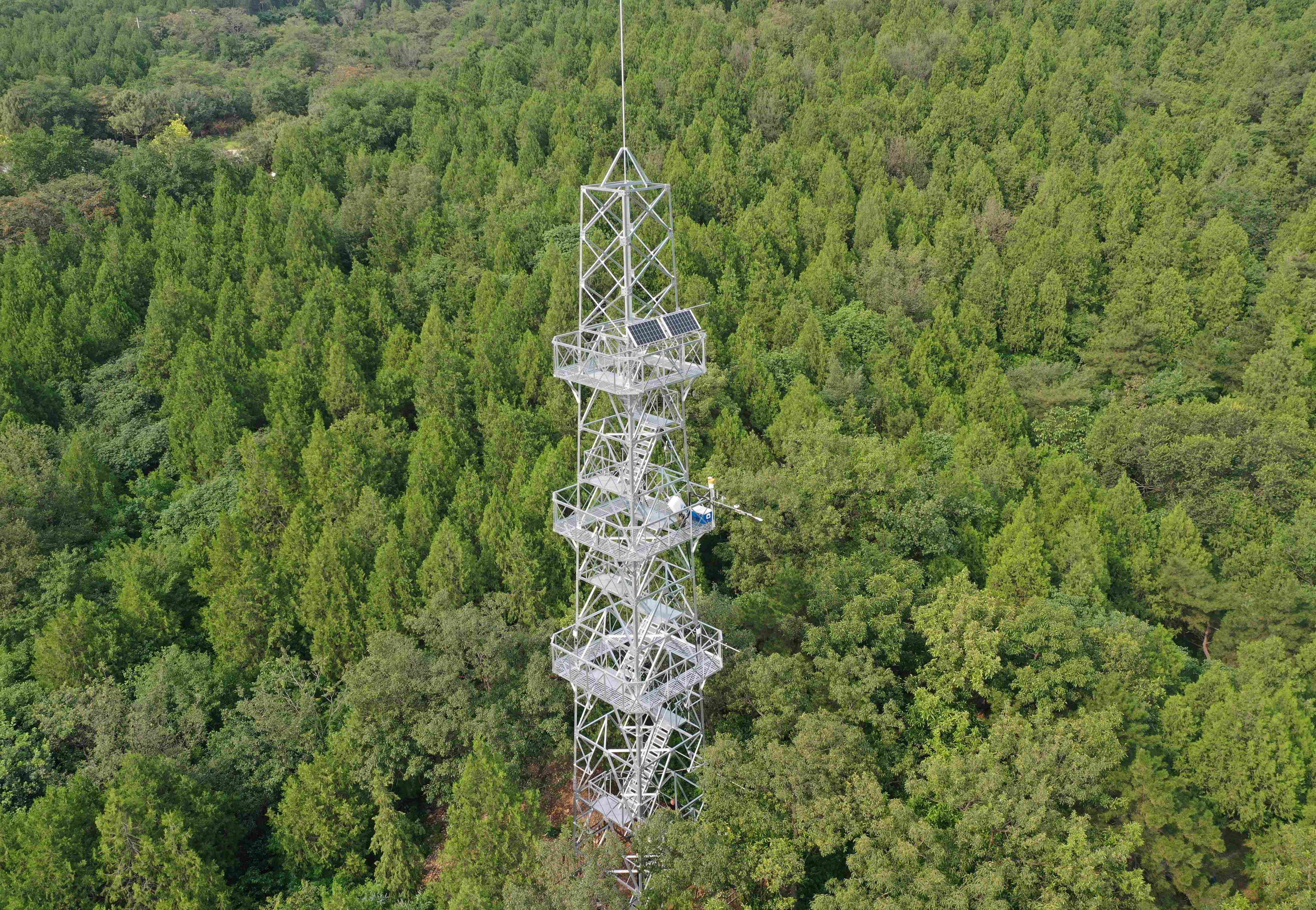

- Team: Beijing Forestry University | Beijing
- PI: Dr. Tianshan Zha, Dr. Peng Liu, Dr. Xin Jia
Shisanling Arborvitae Ecosystem Observation Station (SSLA) is located in the Mangshan National Forest Park, Changping District, Beijing (40°15'53? 116°15'47?, 659 m a.s.l.), as a member of the Beijing Landscaping Ecosystem Observation Network (BJLEN). The site is characterized by a warm temperate monsoonal continental climate, with a mean annual temperature of 12?, a frost-free period of 250 days per year, and a mean annual precipitation of 612 mm. The vegetation type is evergreen coniferous forest dominated by Platycladus orientalis, which has a mean height of 16 m and a mean diameter at breast height (DBH) of 34.5 cm. The understory consists of Amygdalus triloba, Forsythia suspensa and Jasminum nudiflorum. The soil is of the cinnamon type. Measurements at SSLA include eddy-covariance fluxes (ecosystem carbon, water and energy exchange), environmental variables (air temperature and humidity, radiation, soil temperature and soil moisture, etc.), air quality variables (PM2.5, PM10, NOx, SO2, CO, O3 and negative oxygen ions) and sap flow rates (transpiration). Measurements at SSLA started in January, 2021.

- Team: Beijing Forestry University | Beijing
- PI: Dr. Tianshan Zha, Dr. Peng Liu, Dr. Xin Jia
Baihuashan Larch Ecosystem Observation Station (BSHL) is located in the southwest fringe of the Baihuashan National Nature Reserve, Mentougou District, Beijing (39°50'12?N, 115°34'42?E, 1151 m a.s.l.), as a member of the Beijing Landscaping Ecosystem Observation Network (BJLEN). The site is characterized by a warm temperate monsoonal continental climate, with a mean annual temperature of 6.3 ?, a frost-free period of 110 days per year, and a mean annual precipitation of 450-750 mm. The vegetation type is deciduous coniferous forest dominated by Larix principis-rupprechtii, which has a mean height of 19.2 m and a mean diameter at breast height (DBH) of 21.1 cm. The soil is of the cinnamon type. Measurements at MYP include eddy-covariance fluxes (ecosystem carbon, water and energy exchange), environmental variables (air temperature and humidity, radiation, soil temperature and soil moisture, etc.), air quality variables (PM2.5, PM10, NOx, SO2, CO, O3 and negative oxygen ions) and sap flow rates (transpiration). Measurements at BSHL started in July, 2021.
- Team: Chinese Academy of Forestry
- PI: Dr. Xudong Zhang 张旭东
The Yueyang Poplar Plantation is a 60 ha area located on the floodplain in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River with coordinates 29°31'35"N, 112°55'22"E. This site is in the subtropical region of China, with a long-term, mean annual temperature of 16.8°C and a mean annual precipitation of 1400 mm. The soil was fluvo-aquic soil. Generally, the field was inundated for about 20–50 days a year, with the longest record of 130 d. The old plantation was established in 2000 with different poplar clones of Populus dettoides, and was clear-cut in 2011. The new plantation was established in 2012. The dominant understory species of the old plantation was Leonurus arternisia, with a coverage of ~90%. Methane flux was also observed for 3 years after clear-cutting.
Grassland Ecosystems

- Team: Southwest University, China | Heihe Remote Sensing Experimental Research Station, Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences
- PI: Dr. Che Tao
A'Rou Superstation is an alpine grassland ecosystem flux observation site, affiliated with the Heihe Remote Sensing Experimental Research Station, Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAREERI, CAS). This station is located in the Caodaban village, A'rou Town, Qilian County, Qinghai Province. The site coordinates are 38°02'50.3"N, 100°27'51.6"E, 3033 m. The underlying surface is a cold grassland surface, which is the typical grassland in the Qilian Mountains.
The A'rou Superstation is located in the hinterland middle of Qilian Mountain where the climate has a typical plateau continental climate. Its annual average temperature is 0.7°C, annual average precipitation is 400 mm, annual evaporation varies from 1100 mm to 1500 mm, extreme maximum temperature is 30.5°C, extreme minimum temperature is -31.0 °C , annual snowfall period is 240-270 days, the frozen period begins in September and finishes in May of next year, and the frostless season is about 110 days.
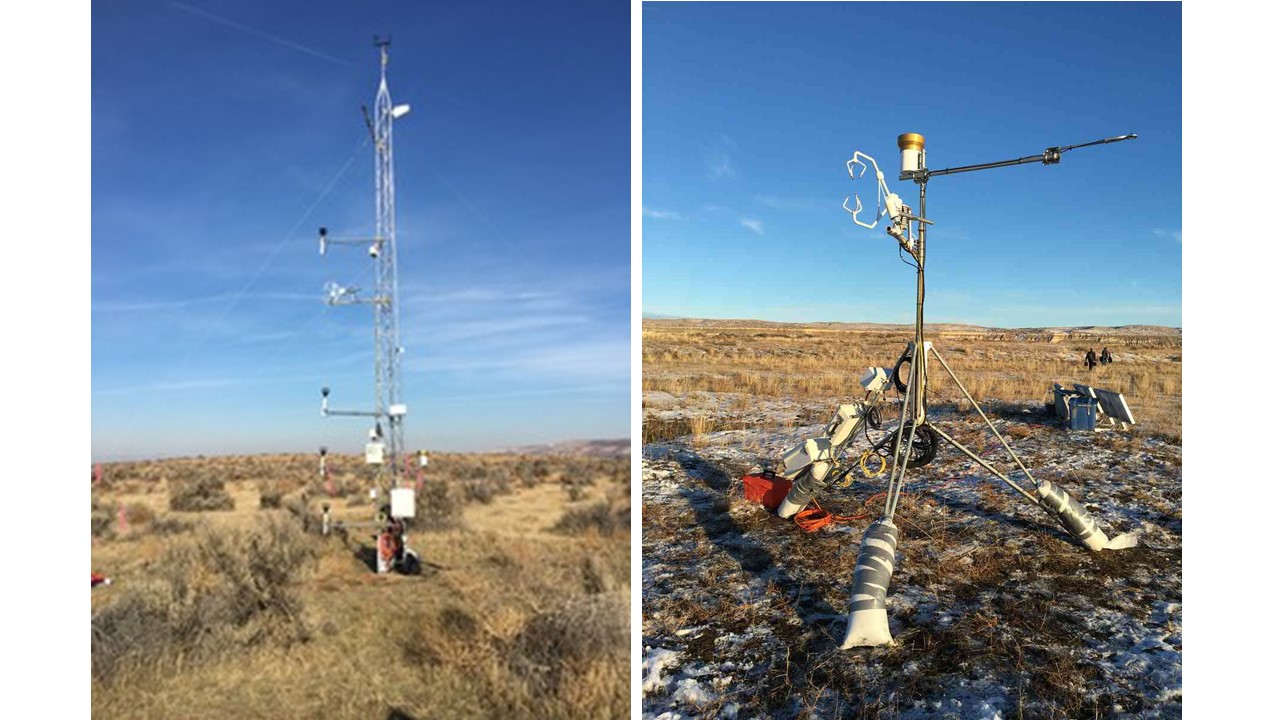

- Team: Washington State University and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (Dr. Heping Liu, Dr. Xingyuan Chen)
The two sites are distinct semiarid ecosystems characterized by different levels of groundwater availability: an upland sagebrush ecosystem (AmeriFlux site US-Hn1, 46.4089°N, 119.2750°W) and a riparian grassland ecosystem (AmeriFlux site US-Hn2, 46.6889°N, 119.4641°W). The sites have a semiarid climate with a 30-year mean (1986–2015) annual precipitation of 197 mm. The elevation of the upland site is 118.6 m and the elevation of the riparian site is 117.6 m. The upland site is located 0.5 km from the river, at an elevation around 13 m higher than the water surface elevation of the river. The site is characterized by a deep vadose zone, and plant available water is driven by precipitation. Its vegetation is a mixture of shrubs and grasses, including Artemisia tridentata (big sagebrush, 10% cover), Chrysothamnus viscidiflorus (green rabbitbrush, <1% cover), and Bromus tectorum (cheatgrass, 70% cover). The soil texture in the top 30 cm of soil is loamy sand, and the soil texture from 30 to 45 cm depth is sand. The riparian site is located between the river and a slough, at an elevation around 3 m higher than the water surface elevation of the river. The site is characterized by a shallow water table, and plant available water is strongly driven by lateral groundwater-river water exchange. Its vegetation is primarily weedy species such as cheatgrass (40% cover), Salsola kali (Russian thistle, 5% cover), and Centaurea repens (diffuse knapweed, 5% cover), but also includes native grasses such as Sporobolus cryptandrus (sand dropseed; <1% cover), Poa bulbosa (bulbous bluegrass; <1% cover), and Agropyron dasystachyum (thickspike wheatgrass; <1%). Soil texture in the top 45 cm of soil is sand. The instruments in the two sites are listed in Table 1 below.
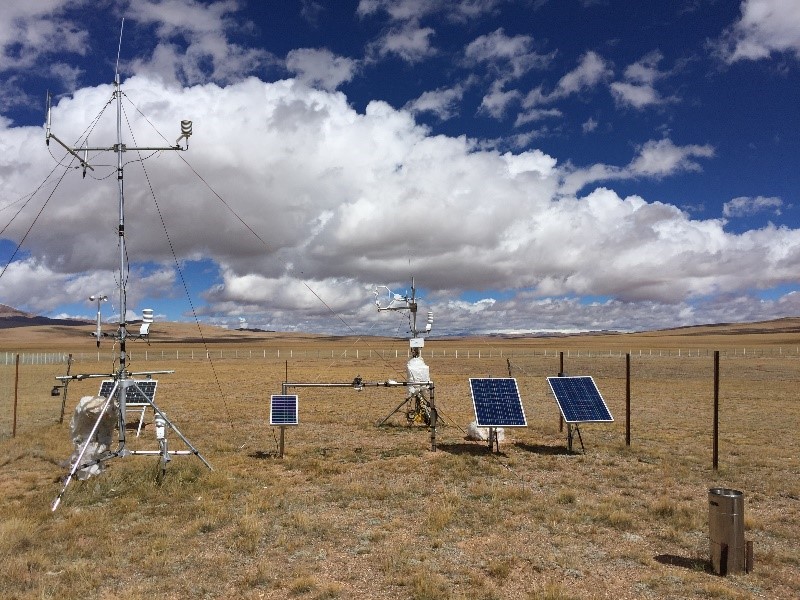

- Team: Chinese Academy of Sciences (Dr. Yinsheng Zhang and Dr. Ning Ma)
The Shuanghu Alpine Steppe Station (33.22°N, 88.83°E) is located in the hinterland of Qiangtang Plateau. The elevation is 4947 m above sea level. The mean annual temperature is ca. -4 °C, with July temperatures of about 7 °C, down to approximately -15 °C in January. Multiyear mean annual precipitation is about 350 mm. The dominant vegetation type is cold-xerophytic C3 grasses such as stipa purpurea and carex moorcroftii. In the growing season, the mean canopy height is about 0.03 m. The soil belongs to sandy loam.
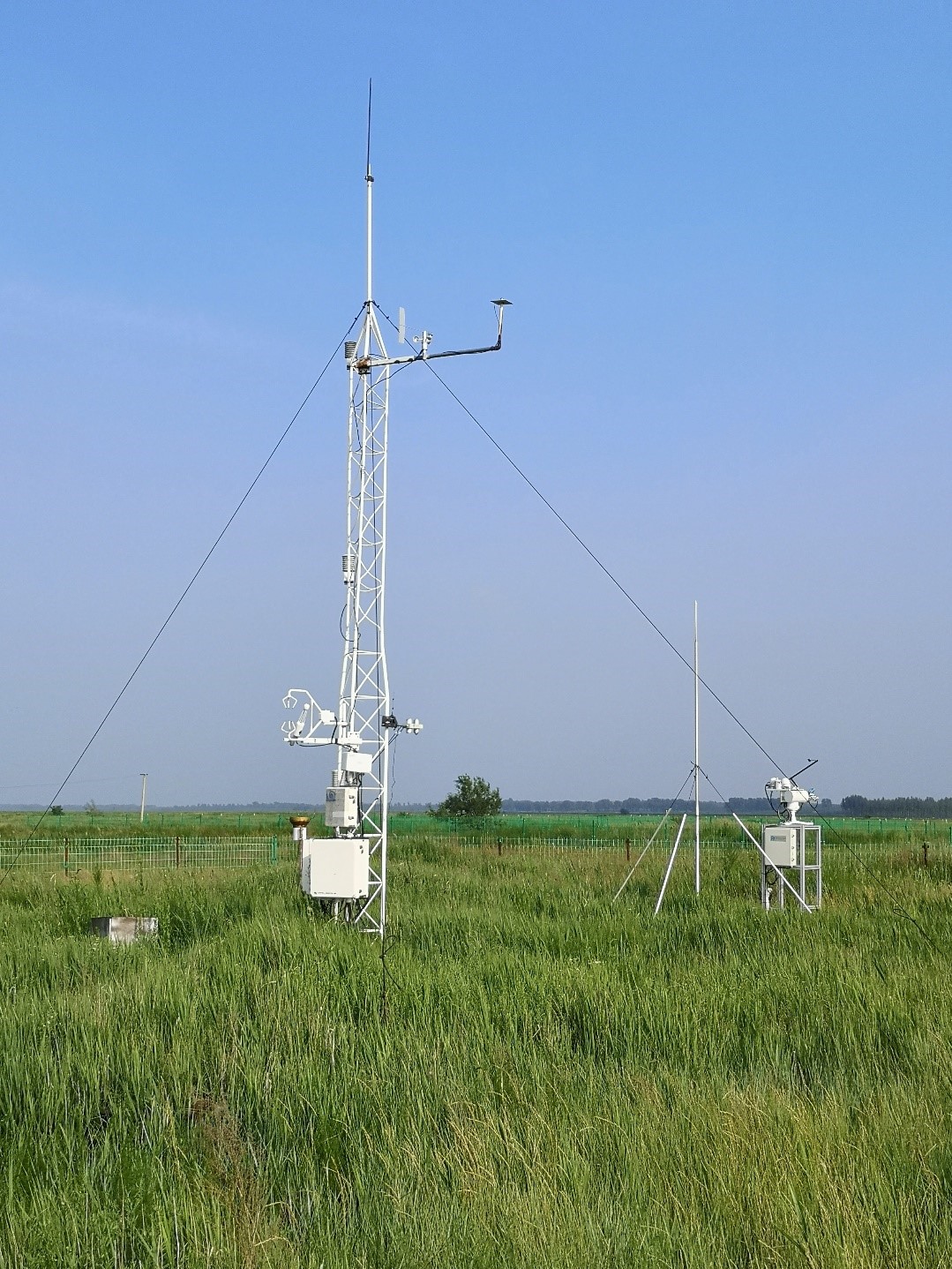

- Team: Northeast Normal University (Dr. Shicheng Jiang)
The fenced meadow site is 10 km around the Songnen Grassland Ecology Field Station of the Northeast Normal University in Changling, Jilin, China (123°30'33?E, 44°35'37?N, 141 m a.s.l.). This site was established in July 2007. This site has a temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The mean annual air temperature is 4.6 to 6.4°C. Mean annual precipitation is 250 to 500 mm, with 70-80% occurred in May-September. The pan evaporation approximates 1600 mm. And the frost-free period ranges from 130 to 165 days. The soil type of study site is alkali-saline with a soil texture of 23% sand, 35% silt and 42% clay, which is classified as a Salic Solonetz in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (IUSS Working Group, 2015) and an Aqui-Alkalic Halosol in the Chinese soil taxonomic system. The soils contain high content of free sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), and the pH of the soils is between 8.0 and 11.0. The dominant native plants are Leymus chinensis and Phragmitis communis. Community coverage of undisturbed grassland could reach 60~90%, with 100~200 g m-2 standing biomass.
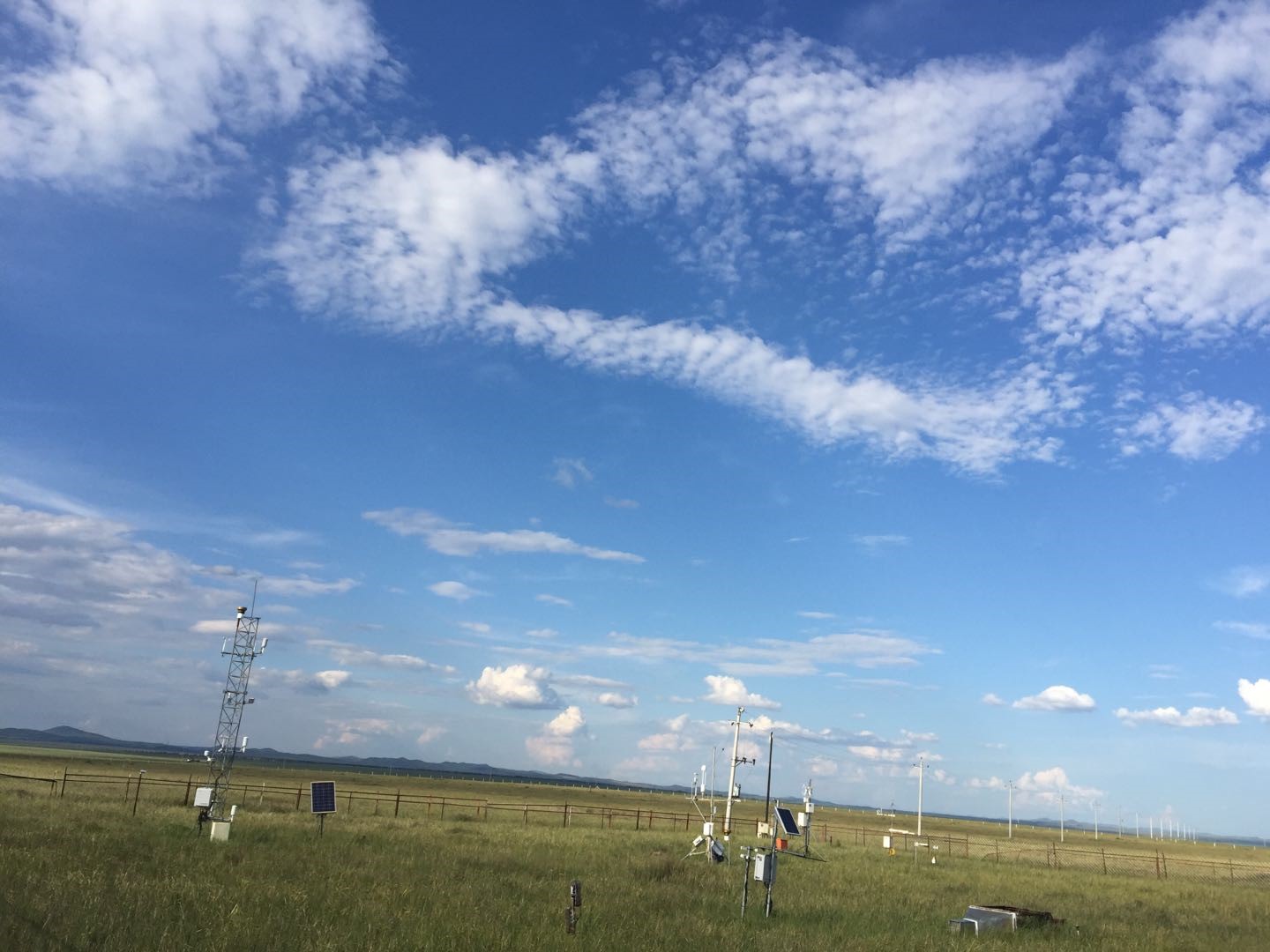

- Team: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Xiaoping Xin and Xu Wang)
The fenced meadow observation site is located in National Hulunber Grassland Ecosystem Observation and Research Station in Hailar, Inner Mongolia, China (120°07'09? E, 49°21'05? N, 665 m a.s.l.). This site was established in 2008. This site has a mid-temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The mean annual air temperature is 2.4°C with annual cumulative temperature of 1580~1800 °C. Mean annual precipitation is 390 mm, with 70%-80% occurred in July-September. The frost-free is around 110 days. Constructive species are Leymus chinensis, Stipa baicalensis, Cleidtogenes squarrosa, and companion species Vicia amoena and Poa atensis. The soil type of study site is dark chestnut soil.
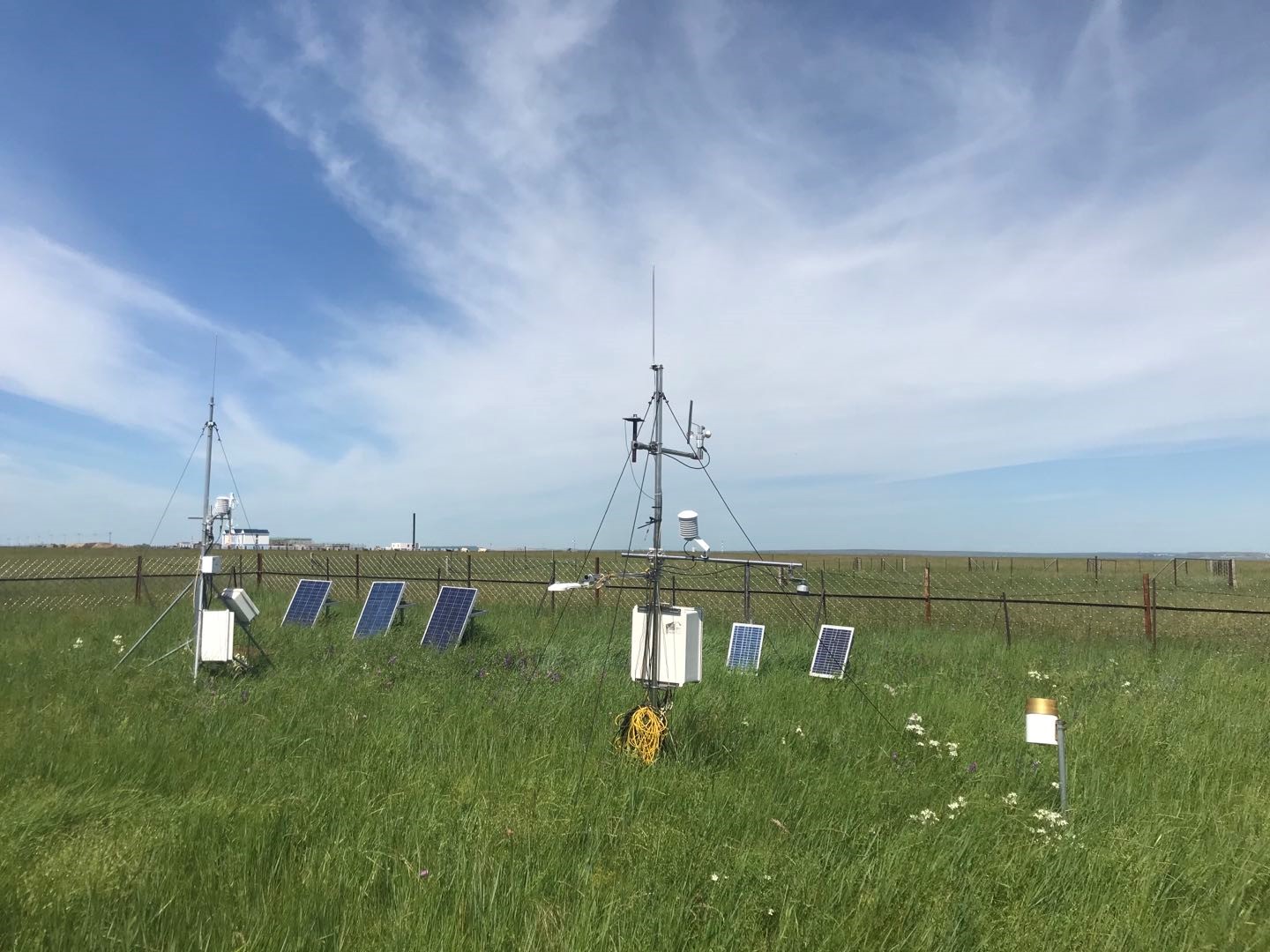

- Team: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Xiaoping Xin and Xu Wang)
The grazed meadow observation site is located in National Hulunber Grassland Ecosystem Observation and Research Station in Hailar, Inner Mongolia, China (120°02'23? E, 50°11'58? N, 552 m a.s.l.). This site was established in 2010. This site has a mid-temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The mean annual air temperature is 2.4°C with annual cumulative temperature of 1580~1800 °C. Mean annual precipitation is 390 mm, with 70-80% occurred in July-September. The frost-free is around 110 days. The dominant species are Leymus chinensis, Stipa baicalensis, Cleidtogenes squarrosa, with companion species Vicia amoena and Poa atensis. Each year grazing is from mid-May to mid-October by cattle. The soil type of study site is dark chestnut soil.
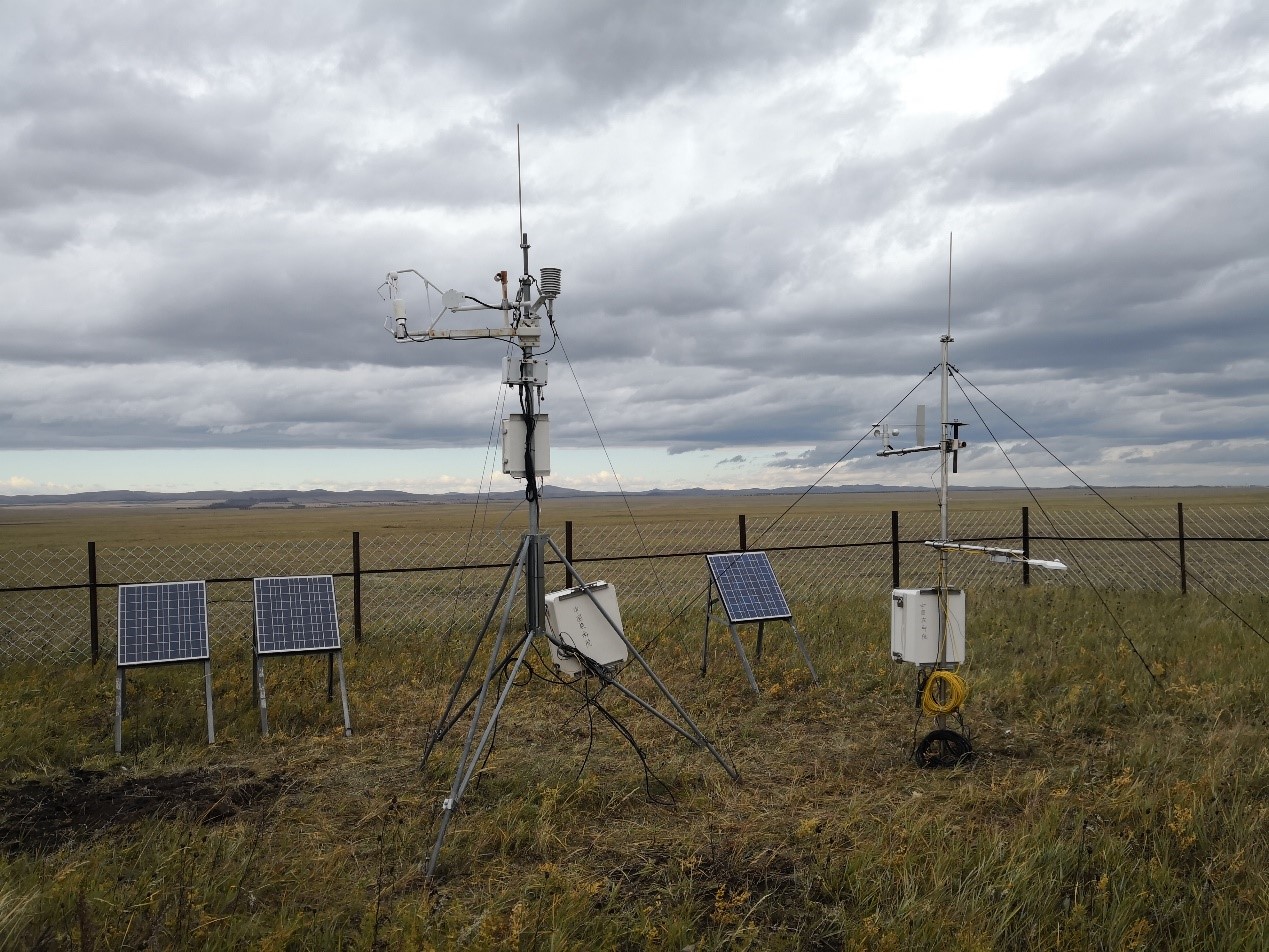

- Team: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Xiaoping Xin and Xu Wang)
The mowed meadow observation site is located in National Hulunber Grassland Ecosystem Observation and Research Station in Hailar, Inner Mongolia, China (120°08'20? E, 49°21'25? N, 664 m a.s.l.). This site was established in 2010. This site has a mid-temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The mean annual air temperature is 2.4°C with annual cumulative temperature of 1580~1800 °C. Mean annual precipitation is 390 mm, with 70-80% occurred in July-September. The frost-free is around 110 days. The dominant species are Leymus chinensis, Stipa baicalensis, Cleidtogenes squarrosa, with companion species Vicia amoena and Poa atensis. Each year mowing is around mid-August. The soil type of study site is dark chestnut soil.

- Team: Northeast Normal University (Dr. Shicheng Jiang)
The fenced meadow site is 10 km around the Songnen Grassland Ecology Field Station of the Northeast Normal University in Changling, Jilin, China (123°30'33?E, 44°35'37?N, 141 m a.s.l.). This site was established in July 2007. This site has a temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The mean annual air temperature is 4.6 to 6.4°C. Mean annual precipitation is 250 to 500 mm, with 70-80% occurred in May-September. The pan evaporation approximates 1600 mm. And the frost-free period ranges from 130 to 165 days. The soil type of study site is alkali-saline with a soil texture of 23% sand, 35% silt and 42% clay, which is classified as a Salic Solonetz in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (IUSS Working Group, 2015) and an Aqui-Alkalic Halosol in the Chinese soil taxonomic system. The soils contain high content of free sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), and the pH of the soils is between 8.0 and 11.0. The dominant native plants are Leymus chinensis and Phragmitis communis. Community coverage of undisturbed grassland could reach 60~90%, with 100~200 g m-2 standing biomass.
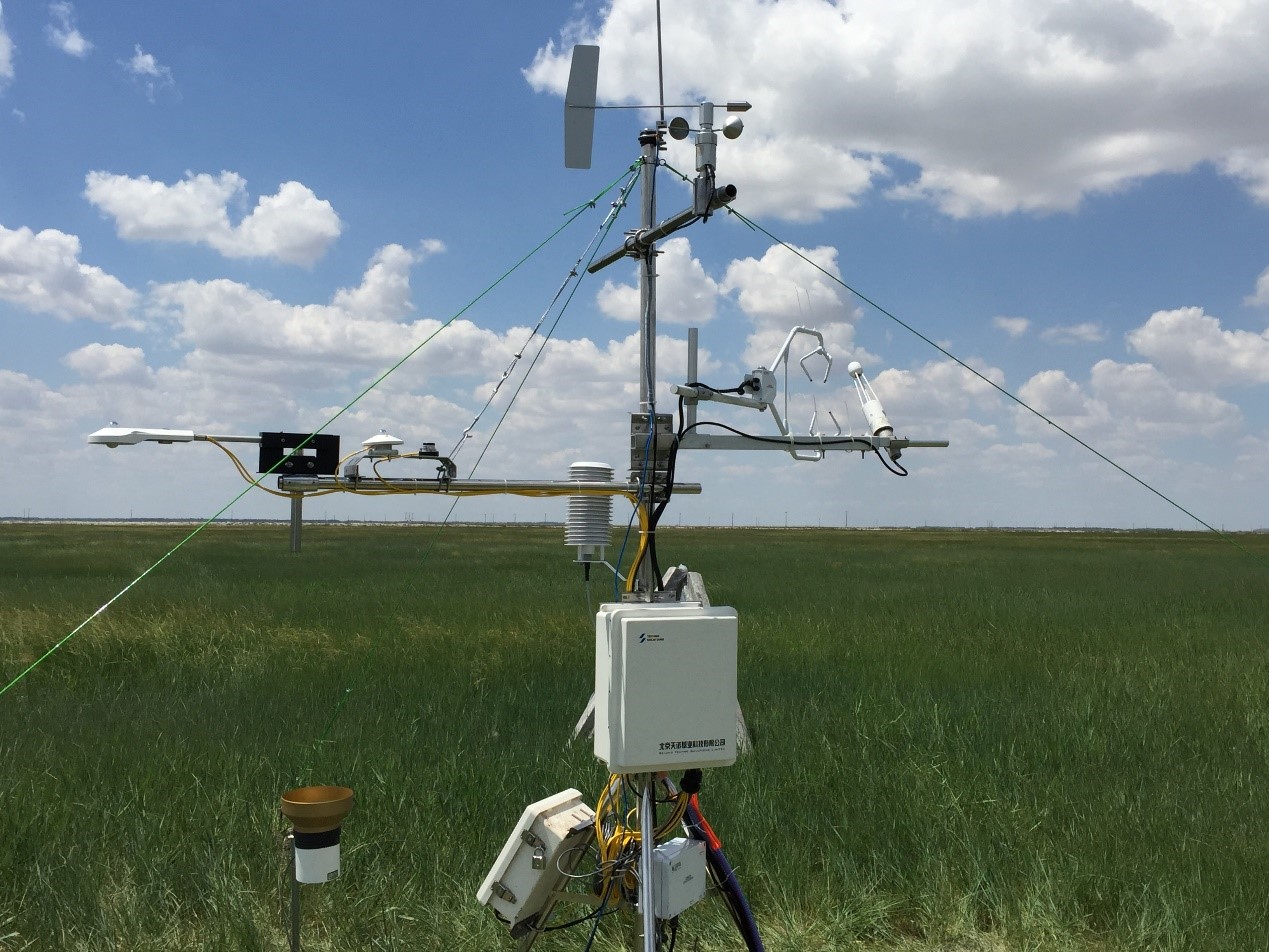

- Team: Shanxi University (Dr. Gang Dong)
The clipped meadow site is located in Changling, Jilin, China (123°32'15?E, 44°39'01?N, 139 m a.s.l.). This station was established in June 2018. The climate is a temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate, with an average annual temperature of 4.6 to 6.4°C. The mean annual precipitation is 250 to 500 mm. The pan evaporation approximates 1600 mm. The frost period lasts for 130 to 165 days. The soil is alkali-saline soil, the content of free sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), and the pH from 8.0 and 11.0. The dominating specie is Leymus chinensis. Clipping was conducted once a year at the middle of August.
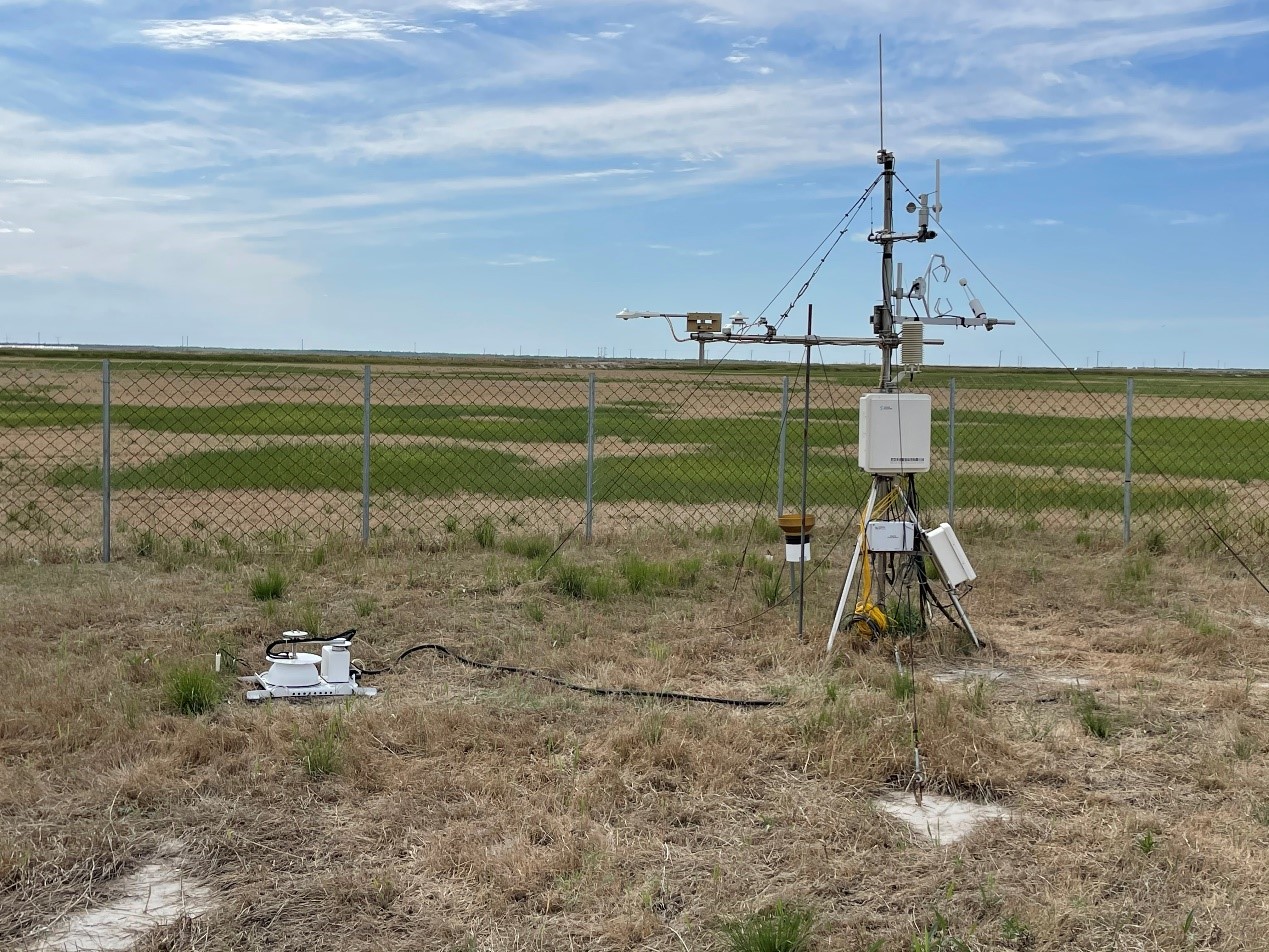

- Team: Shanxi University Dr. Gang Dong)
The degraded alkali-saline land is located in Changling, Jilin, China (123°32'18?E, 44°38'40?N, 140 m a.s.l.). This station was established in June 2018. The station belongs to the temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The long-term mean annual air temperature of the station is 4.6 to 6.4°C. The mean annual rainfall varies between 250 to 500 mm, with the frost-free period ranges from 130 to 165 days. Soil is alkali-saline soil. The dominant species is Chloris virgate. The eddy covariance includes an open-path infrared gas analyzer (IRGA, LI-7500, LI-COR Inc., USA) and a CSAT3 three-dimensional sonic anemometer (CSAT3, Campbell Scientific Inc., CSI, USA). The eddy covariance and micrometeorological measurements mounted 2.0 m above the ground to calculate the net exchange of CO2, H2O, energy between the vegetation and the atmosphere. Soil respiration are measured with a common IRGA system (LI-8100, LI-COR Inc., USA).
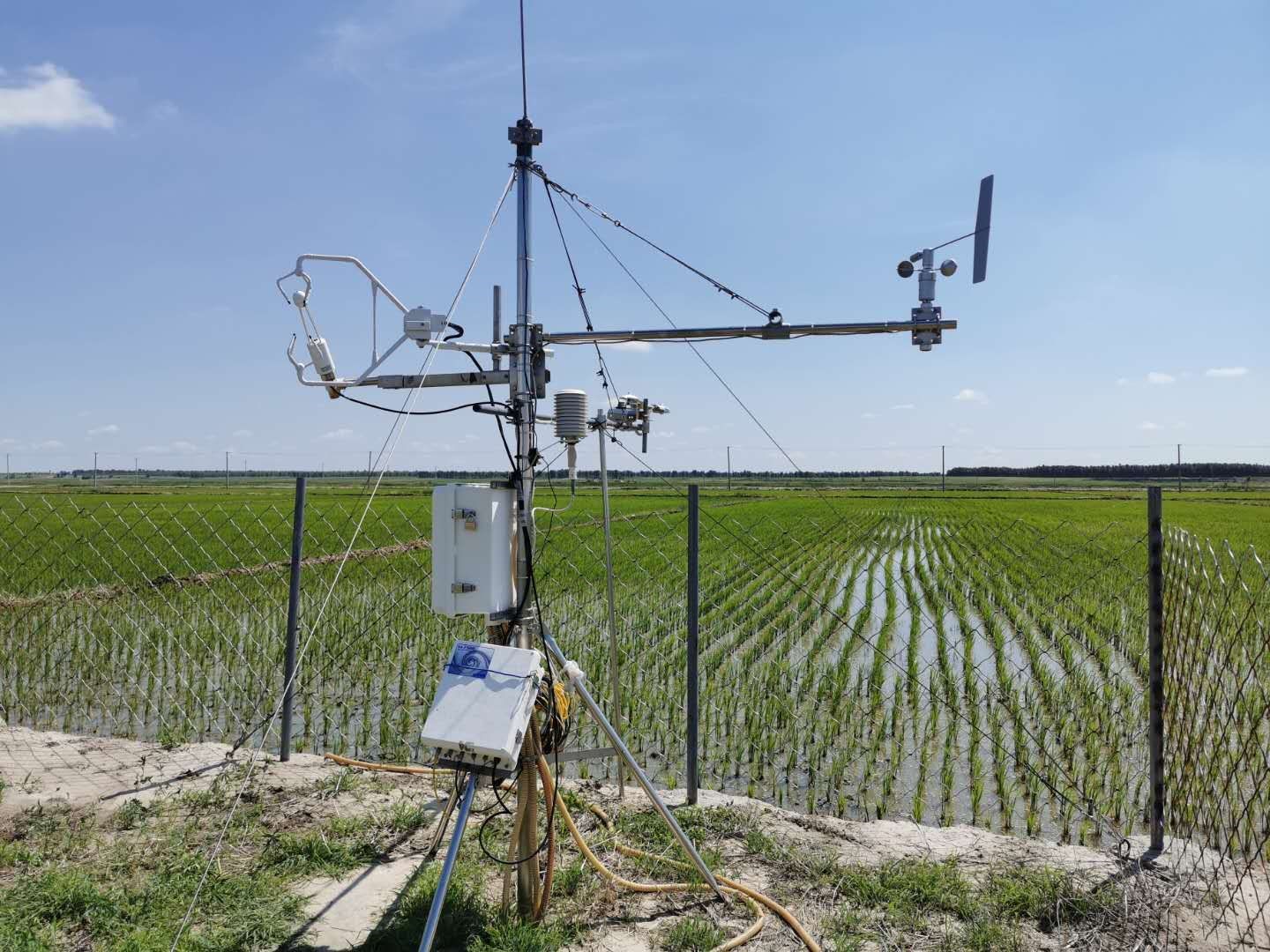

- Team: Shanxi University Dr. Gang Dong)
The rice paddy field site (123°28'13?E, 44°35'48?N, 143 m a.s.l.) is located in Changling, Jilin, China. This site was established in June 2018. This site has a temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The mean annual air temperature is 4.6 to 6.4°C. Mean annual precipitation is 250 to 500 mm. The soil type is alkali-saline with a soil moisture of 80%. Water source mainly comes from groundwater. The dominating specie is Oryza sativa. Rice was cultivated once a year in late spring and harvested at the end of Autumn. Before the reclamation, the area is alkali-saline meadow.

- Team: Shanxi University Dr. Gang Dong)
The maize field site is located in Changling, Jilin, China (123°31'57?E, 44°33'11?N, 141 m a.s.l.). This station was established in June 2019. The station belongs to the temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The long-term mean annual air temperature of the station is 4.6 to 6.4°C. The mean annual rainfall varies between 250 to 500 mm, with the frost-free period ranges from 130 to 165 days. The soil type of study site is alkali-saline. The dominant species is Zea mays. Before the reclamation, the area is alkali-saline meadow.
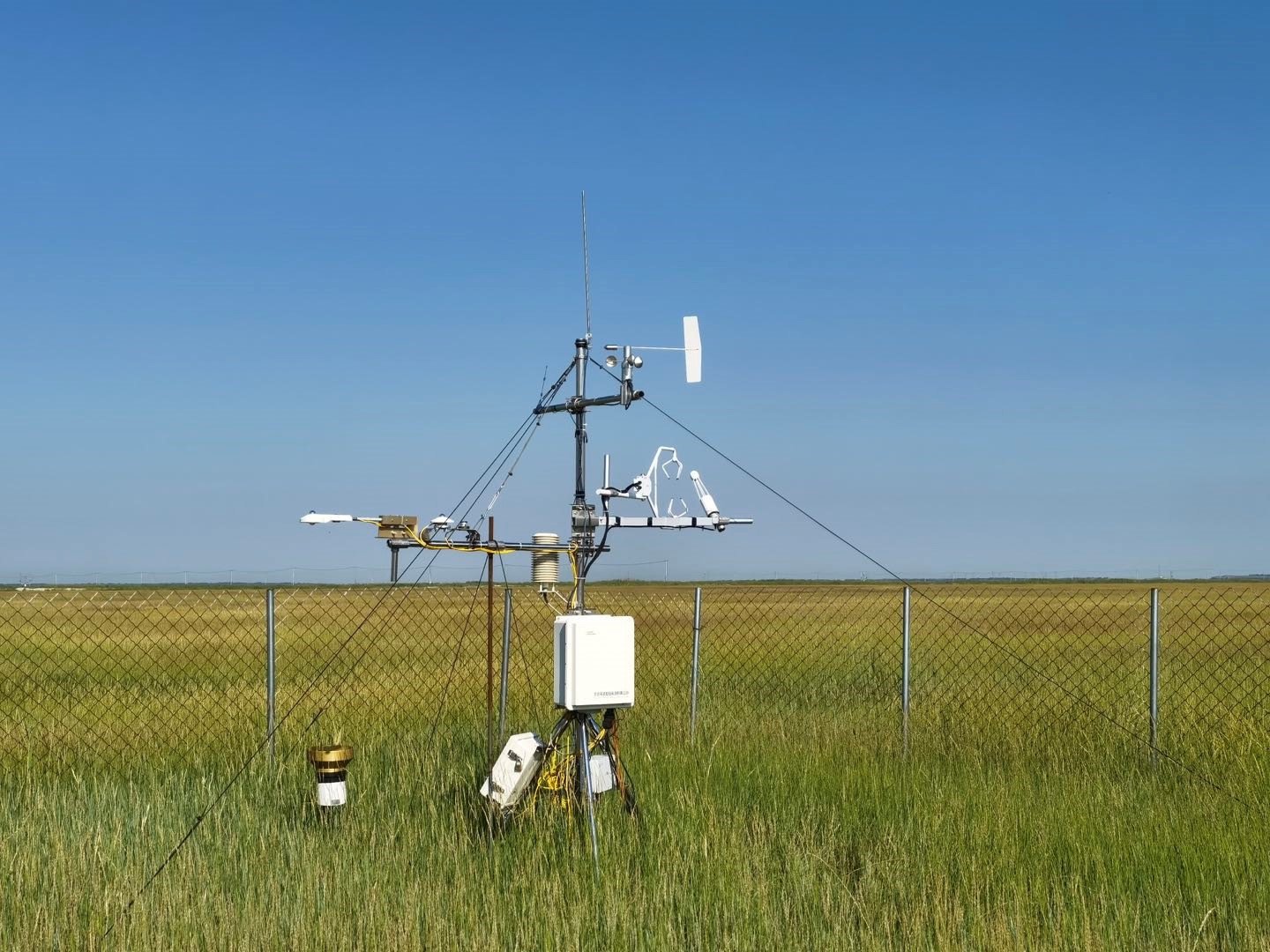

- Team: Shanxi University Dr. Gang Dong)
The clipped meadow site is located National Hulunber Grassland Ecosystem Observation and Research Station in Hailar, Inner Mongolia, China (119°59'31?E, 49°19'51?N, 632 m a.s.l.). This site was established in June 2018. This site has a mid-temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The mean annual air temperature is 2.4°C with annual cumulative temperature of 1580~1800 °C. Mean annual precipitation is 390 mm, with 70-80% occurred in July-September. The frost-free is around 110 days. Constructive species are Leymus chinensis, Stipa baicalensis, Cleidtogenes squarrosa, and companion species Vicia amoena and Poa atensis. And clipping was conducted once a year at the end of August. The soil type of study site is dark chestnut soil.
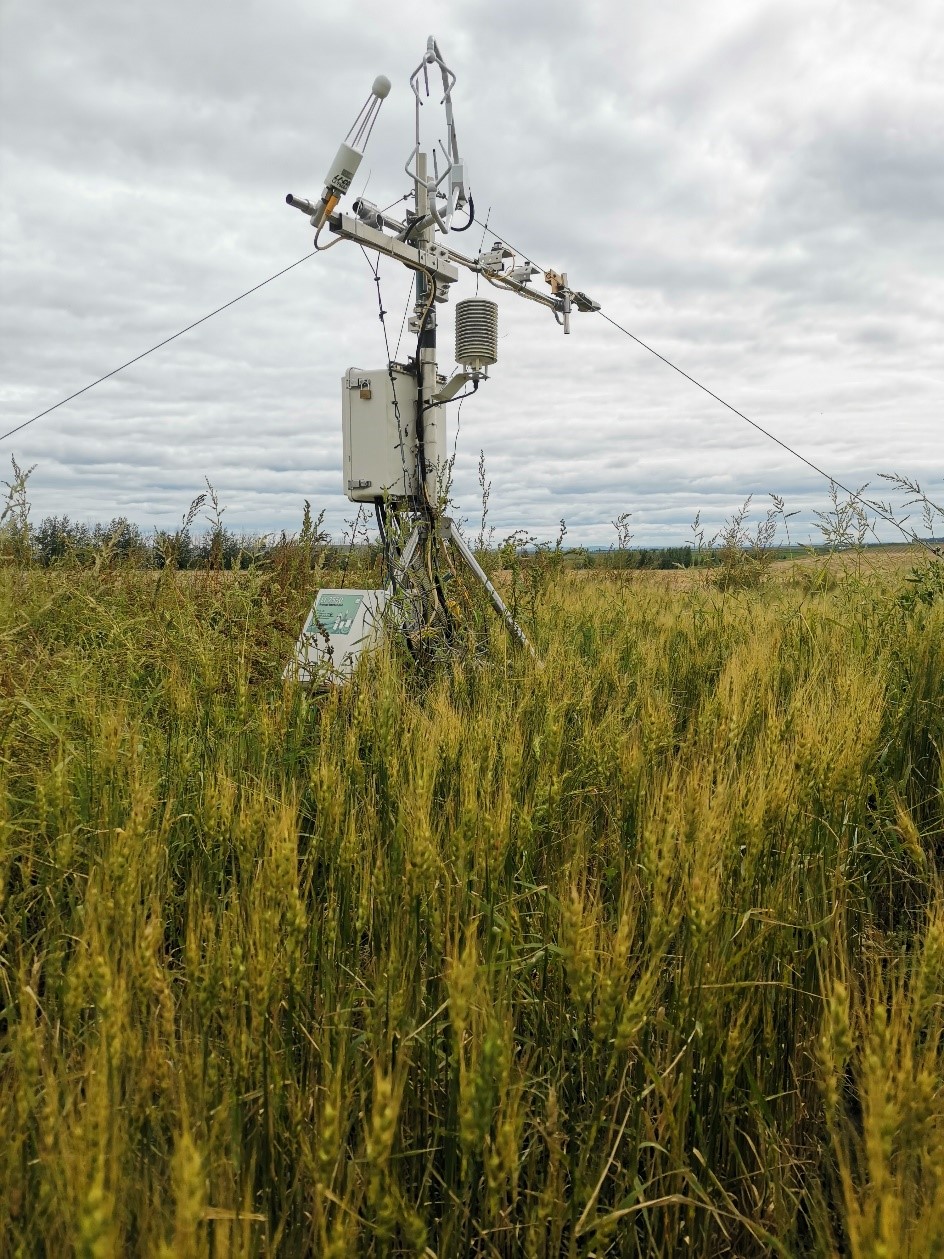

- Team: Shanxi University Dr. Gang Dong)
The rotated crop site is located National Hulunber Grassland Ecosystem Observation and Research Station in Hailar, Inner Mongolia, China (120°00'48?E, 49°20'19?N, 631 m a.s.l.). This site was established in June 2018. This site has a mid-temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate. The mean annual air temperature is 2.4°C with annual cumulative temperature of 1580~1800 °C. Mean annual precipitation is 390 mm, with 70-80% occurred in July-September. The frost-free is around 110 days. The dominant species are two crops of Triticum aestivum, Brassica campestris and Solanum tuberosum in rotation. The soil type of study site is dark chestnut soil.
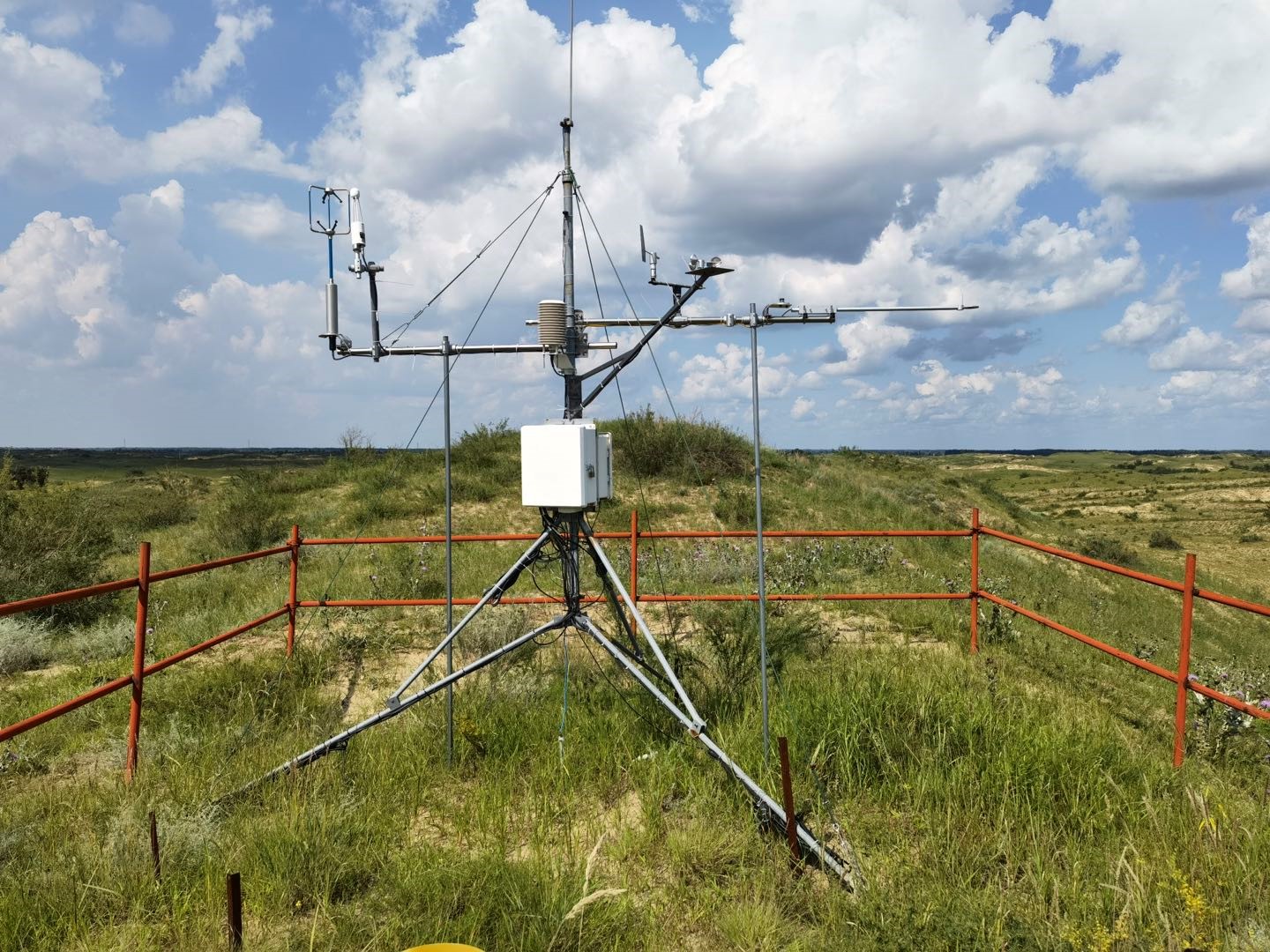

- Team: Shanxi University Dr. Gang Dong)
The site is a sandy shrubland in the Horqin Sandy Land, at Tongliao, Inner Mongolia, China (122°17'32?E, 43°4'35?N, 251 m a.s.l.). The terrain is near flat, has a continental semiarid monsoon temperate climate regime. The mean annual temperature is 6.8 °C, with mean monthly temperatures ranging from -9.63 °C in January to 24.58 °C in July. Average annual precipitation is approximately 360 mm, with about 70 % of the precipitation occurring during the growing season between June and August. Annual mean potential evaporation is approximately 1973 mm. The annual frost-free period is 130 to 150 d. The most common soil type in the study region is a sandy soil. Vegetation cover in the study area ranged from 50 % to 70 %. The dominant plant species were annual herbs dominated by Artemisia halodendron Turcz.et Bess.
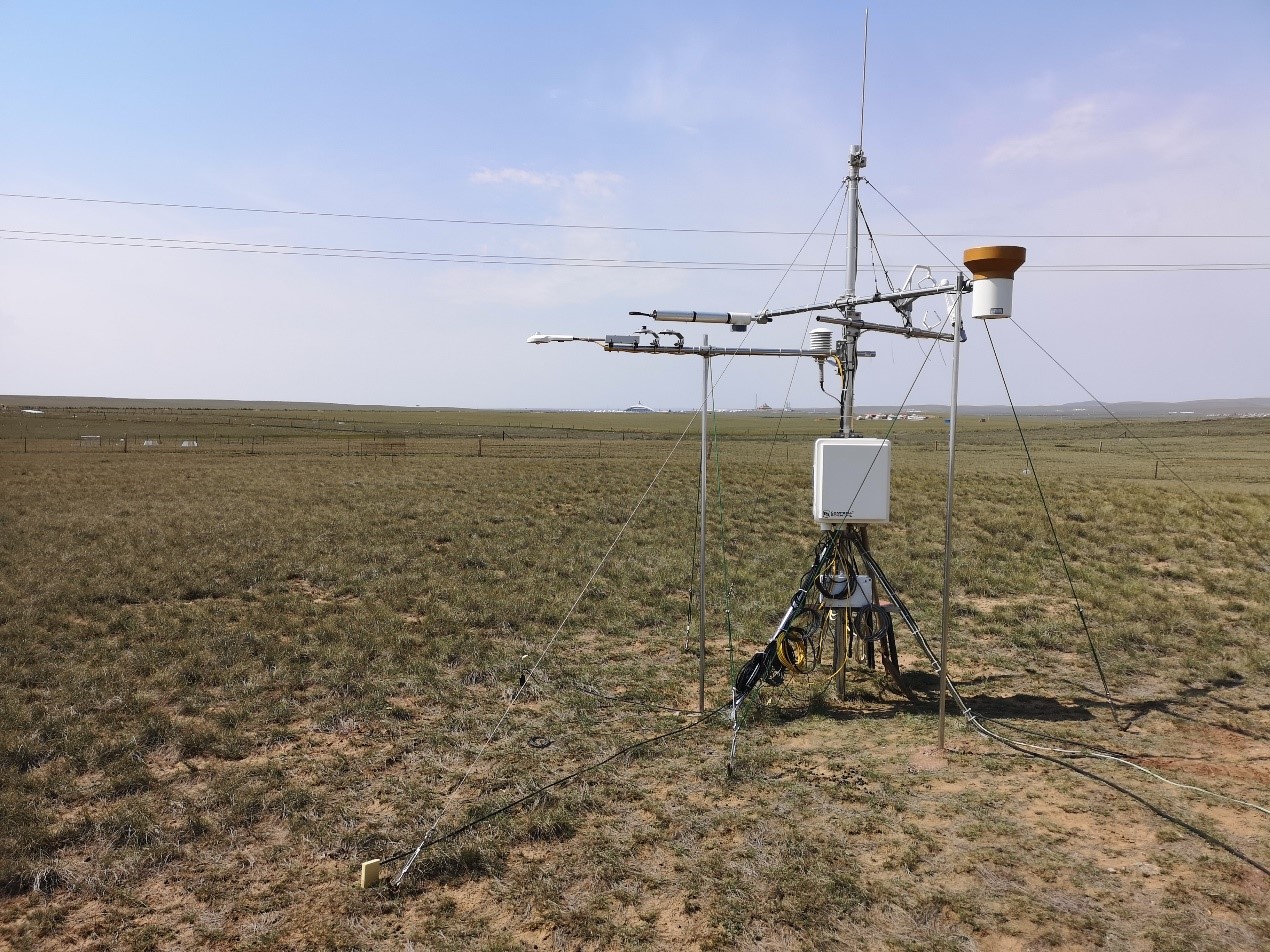

- Team: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
The grazed desert steppe site is at the Siziwang Experimental Station of the Inner Mongolia Academy of Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Sciences in Siziwang, Inner Mongolia, China (118°53'26?E, 41°47'25?N). The region belongs to the mid-temperate zone and has a distinct continental climate. Winters (November–late April) are cold, dry and windy. The spring season, from later April or early May to June, is generally windy and dry. Summers (June–September) are warm and relatively rainy. The long-term mean annual air temperature of the region is 6.7 ?C, with the highest monthly mean temperature in July (22.6 ?C) and the lowest in January (-11.6 ?C, average of 1971–2000). The mean annual rainfall is 180 mm but varies from one year to another with strong seasonal variability (up to 60% variation). Frequent droughts are usually the limiting factor for plant growth. The soil is a light-colored Chernozemic soil (Chinese System of Soil Classification 2001) and equivalent to Cryolls (USDA Soil Classification System). The mean ± SD of soil organic carbon (SOC) in the 0-0.1 m layer is 14.03 ± 0.64 g kg-1. The site has relatively homogenous vegetation and is dominated (area coverage >85%) by perennial bunchgrass (Stipa breviflora Griseb). The grazing experiment begun from June 2004. The fetch for the flux measurement was 500 m2 × 100 m2 with stocking rate ~ 85%.
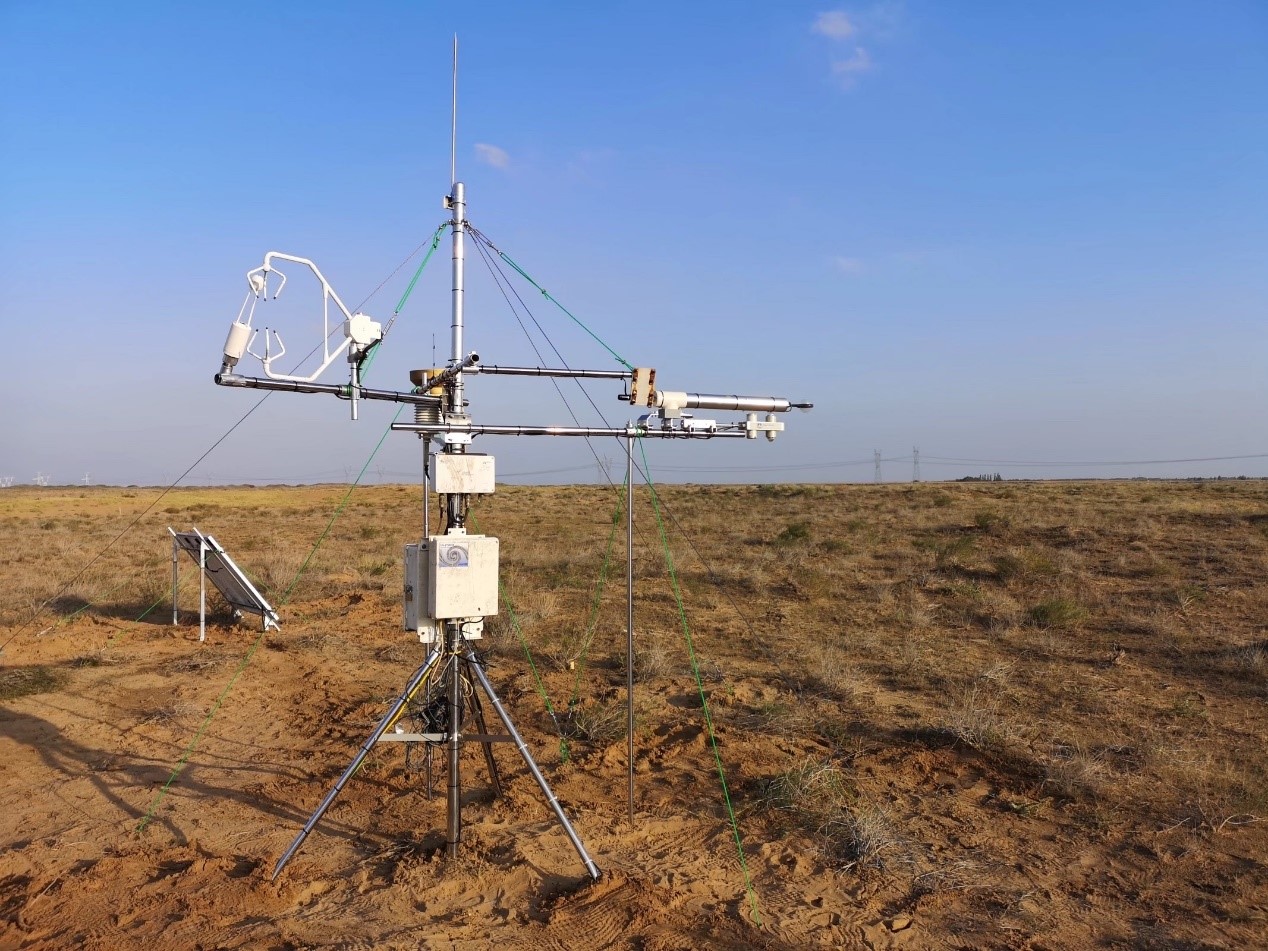

- Team: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
The Ulanbuh desert site is located in the Dengkou of west Inner mongolia Autonomous Region, China (106°44'32?E, 40°25'44?N, 1040 m a.s.l.). The monitoring area is in the northeast of Ulanbuhe desert, with an average altitude of 1040m. Belonging to temperate continental arid climate, the annual natural precipitation and evaporation is145 mm and 2327mm, respectively, most of which occurs from June to September. This accounting for about 60-70% of the annual precipitation. The annual average temperature is 7.8 °C, and the frost-free period is around 136 days. The soil type is aeolian sandy soil with a water content of 2~8 %. The main vegetation types are mainly xeric and super xeric desert vegetation, including Nitraria tangutorum, Artemisia ordosica and Artemisia sphaerocephala.
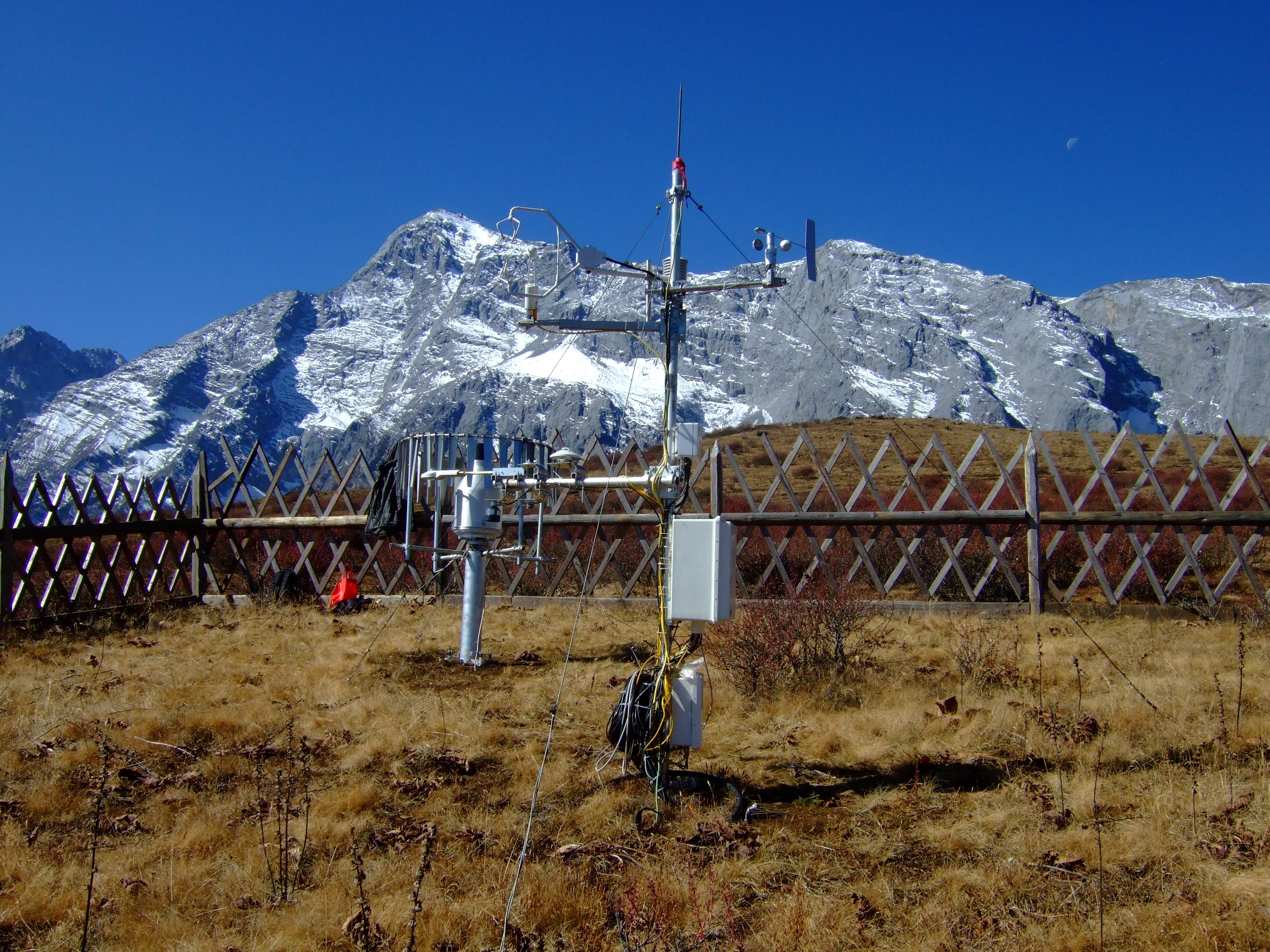

- Team: Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Lijiang observation site (27°10'N, 100°14'E, 3560 m a.s.l.) is located the east of the Yulong Snow Mountain, Lijiang, Yunnan Province in southwest China. The eddy covariance technique was mounted in May 2011. This area is also east of the Hengduan Mountain, where the Yunnan-Guizhou and Qinghai-Tibetan plateaus join. The climate is a subtropical plateau monsoon climate with clear wet and dry seasons, influenced by the southwest and southeast monsoons. The mean annual air temperature in Lijiang City is 12.6°C. The 30-year mean precipitation is 980.3 mm (1981-2010, data from the Lijiang meteorological observation station, 2400 m a.s.l.). Over 85% of the precipitation occurs from June to October. From 1981 to 2010, 37% of days had precipitation of >0 mm d-1for the whole year, and the percentage rose to 60% for the wet season (June to October. The alpine meadow at the observation site is dominated by Kobresia Willd grass with a maximum height of 20 cm and Berberis Linn shrub with a maximum height of over 60 cm. The soil type is dark brown loamy soil. The site has a slope of approximately 10°, with the west higher than the east. There is a coniferous forest 250 m away to the north of the site and the study site is grazed by yaks.
- Team: Grassland Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS)
The typical grassland research station is located in Xilinhot, Inner Mongolia, China (43°44'54.80"N; 115°48'14.24"E). This site was established in 2022. This site has a mid-temperate arid continental climate and the average elevation is 1080 m. The mean annual air temperature is 4.4 °C. Mean annual precipitation is 294 mm. The frost-free is around 110 days. Dominant species are Stipa baicalensis, Leymus chinensis, Caragana, Silver convolvula, Altaiga, Ruthenica ruthenica, Carex, cryptosperma and Astragalus. The soil type of study site is chestnut soil.
- Team: Grassland Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS)
The warm meadow grassland is located in Baiyin Wenduer Gacha, Baiyinhua Town, Xiwuzhumuqin Banner (45°02'52.65"N; 118°55'34.36"E). The average altitude is 1000 m, the average annual temperature is 1.2 ?, the mean annual precipitation is 350 mm, and the annual frost-free period is 105 days. The main type of soil is chestnut soil. Dominant species are Stipa baicalensis, Leymus chinensis, Leymus argus and Artemisia cold, Sedge grass, Bluegrass.
- Team: Grassland Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS)
The warm desert steppeis is located in the Mingan Union Banner of Dalhan (41°46'19"N; 110°34'39"E), located in the northwest of Daqingshan Inner Mongolia Plateau, flat terrain. The elevation is 1367 m above sea level. The mean annual temperature is 4.2 °C. Multiyear mean annual precipitation is about 256.2 mm. The annual frost-free period is 187 days. The main species were Stipa baicalensis, Allium, Leymus leymus, Artemisia cold, Caragana, Allium mongolica. The soil belongs to chestnut soil and brown calcium soil.
Urban Ecosystems
- Urban Ecology and environmental Center, Shanghai Normal University (SHNU)
- PI: Dr. Min Zhao 赵敏
The study area belongs to the subtropical climate, the mean annual air temperature of the region is 15.7°C, the mean annual rainfall is 1160 mm. Under the influence of the east Asian monsoon, the major wind direction is southeast in summer and northwest in winter. The latitude is 3 m or so. The land cover types include vegetation, buildings, roads, water, parking places and so on. The eddy covariance system was set up in a 18 m tower in the campus of Shanghai Normal University (SHNU). Fluxes of CO2 and H2O are measured with an open-path gas analyzer (CAST3, Campbell, USA, CO2 / H2O analyze, Li-7500, LiCor, USA). The micrometeorological measurements (including wind, temperature, humidity etc.) are conducted at four layers every 5 m high from the ground.

- Team: Shanxi University | Taiyuan Urban Wetland Flux (TYUW)
- PI: Dr. Gang Dong, 董刚
The region belongs to the temperate continental monsoon climate. The long-term mean annual air temperature of the region is 9.3°C, with the highest monthly mean temperature in July (22.8 °C). The mean annual rainfall varies between 180 mm and 466.6 mm; and the frost-free period is around 170 days. Soil is alluvial river sand soil. The dominant species in this region are Phragmites australis and Typha orientalis.
The eddy covariance and micrometeorological measurements are conducted in a 5 m tower on an island in the Fenhe River. Fluxes of CO2 and H2O are measured with an open-path gas analyzer (IRGASON, Campbell Scientific, Inc., CSI, UT, USA). The soil CO2 efflux is measured with a soil CO2 flux system (LI-8150 Multiplexer, LI-COR, Inc., Lincoln, NE, USA), leaf photosynthesis is measured with a Portable Photosynthesis System (CIRAS-2, PP systems, USA), and community photosynthesis and respiration are measured with a Portable CO2 analyzer (LI-820, LI-COR, Inc., Lincoln, NE, USA).

- Team: Michigan State University | MSU Campus
- PI: Dr. Jiquan Chen
Michigan State University - known as "the pioneer land grant college"- is located on a 5200 acre campus, incorporating multiple urban to suburban ecosystems alongside industrial regions and green spaces. Residing on land ceded in the 1819 Treaty of Saginaw, Ingham county has an encompassing population within Michigan of 313,000, and 534,000 in its Lansing-East Lansing metro area (U.S Census Bureau). As the only university which houses three medical schools, much of the city of East Lansing's economy revolves around the university. The region (42.7294876N, 84.473649W) in which the tower lies consists of the Grand River, the longest river and second largest watershed in the state, flows through the university's northern region, and much of Lansing-East Lansing. There are more than 20 community and neighborhood parks in East Lansing bordering much of the river, providing protection for the region's urban forest, swamp, as well as diverse flora and fauna. Climate within East Lansing is influenced by the Great Lakes, and thus experiences above average snowfall (46-51 inches) and precipitation days (132). Precipitation is generally greatest during the summer, but is still frequent and significant during winter periods.

- Team: Beijing Forestry University | Beijing
- PI: Dr. Tianshan Zha, Dr. Peng Liu, Dr. Xin Jia
Olympic Forest Park Plantation Observation Station (OPP), a member of the members of the Beijing Landscaping Ecosystem Observation Network, is located in the Chaoyang District of Beijing (40°29'52?N, 116°48'45?E, 1151 m a.s.l.), as a member of the Beijing Landscaping Ecosystem Observation Network (BJLEN). The site is characterized by a warm temperate monsoonal continental climate, with a mean annual temperature of 12.5 ?, a frost-free period of 190 days per year, and a mean annual precipitation of 600 mm. The vegetation type is evergreen coniferous forest dominated by Pinus tabulaeformis, which has a mean height of 7.7 m and a mean diameter at breast height (DBH) of 20.6 cm. The understory consists mainly of Prunus davidiana, Amygdalus triloba and Swida alba Opiz. The soil is of the fluvo-aquic type. Measurements at OPP include eddy-covariance fluxes (ecosystem carbon, water and energy exchange), environmental variables (air temperature and humidity, radiation, soil temperature and soil moisture, etc.) and soil respiration. Measurements at OPP started in January, 2011, and are ongoing.
Wetland Ecosystems

- Team: Fudan University | Global Change and Eco-System, Geo-Information System & Remote Sensing (GC3S)
- PI: Dr. Bin Zhao 赵斌
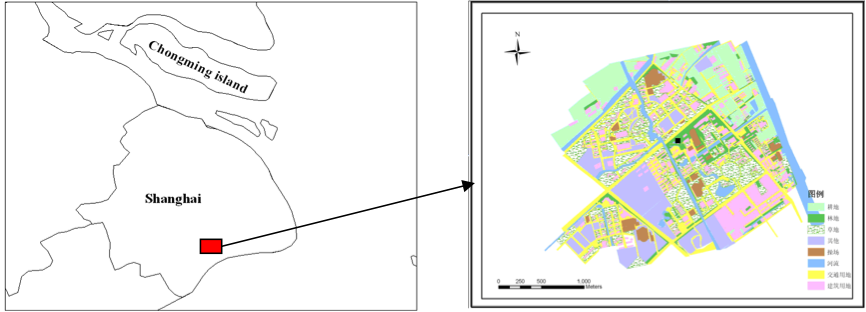
The Dongtan wetland is located in the eastern part of Chongming Island at the estuary of the Yangtze River (31°25'–31°38'N, 121°50'–122°05'E). The inclination of the tidal flat is normally < 1%. The tides here show a mixed semidiurnal pattern. This area has a subtropical monsoon climate. The dominant plant species in Dongtan Wetland include Phragmites australis (native), Spartina alterniflora (invasive) and Scirpus mariqueter (native).
Three eddy flux towers (CMW1, CMW2, CMW3) were established along different elevations and with different vegetation covers in August of 2004. CMW1 was on higher tideland near the dike, CMW3 was on lower tideland near the sea and CMW2 was on mid-level tideland. For each site, CO2, water vapor and energy flux was measured, and an array of meteorological parameters, including solar radiation, PAR, air temperature and relative humidity, net radiation and soil temperature, was also obtained.

- Team: Michigan State University
- PI: Dr. Jiquan Chen
The wetland site is located alongside the Rabbit River and within the Rabbit River Watershed, which extends across ~187,200 acres of rural agricultural and forested land, as well as some urban land primarily across Allegan County of west Michigan, USA. The river originates inland and flows westerly to join the Kalamazoo River, then into Lake Michigan, and hosts four damns. The Hamilton dam, nearest to the tower and the largest dam in the Rabbit River, has a surface area of 28 acres and drains an area of 269 square miles. Soils vary greatly and are composed of glacial deposits including sands, loams, gravel, as well as unsorted glacial till, which contribute to fertile agricultural land. The wetland surrounding the tower location is privately managed by landowners, who regularly monitor water levels and cultivate native plant species for recreation, conservation, hunting and wetland preservation.
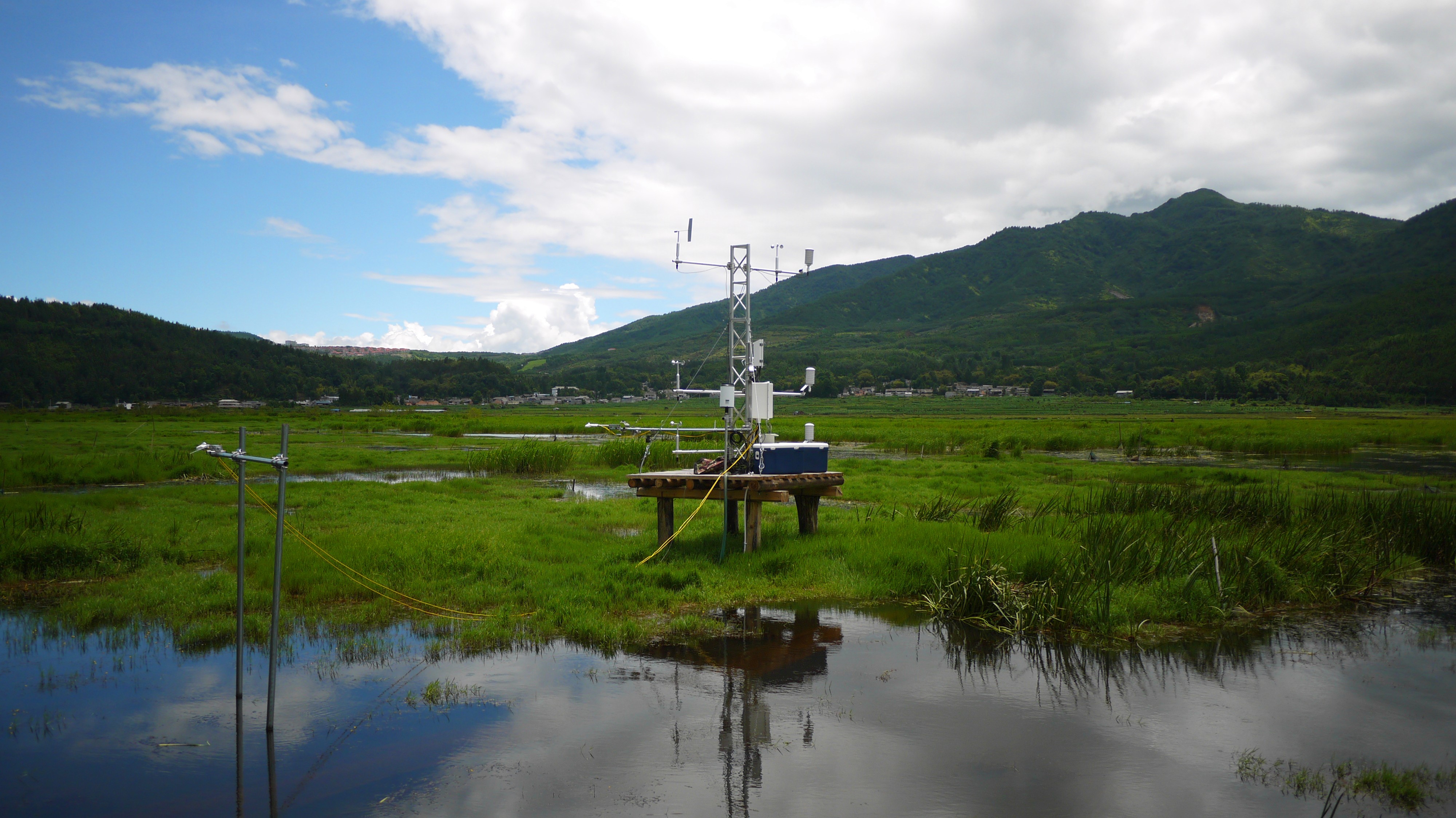

- Team: Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beihai wetland observation site (25°07'N, 98°33'E) is located in the central mountainous area of Tengchong County, in the west part of Yunnan Province, China. This site was established in June 2015. The area has the low cutting landform of middle-mountain in the west slope of Gaoligong Mountain. It is the only natural plateau marsh wetland originated from a volcano created quake lake in the southwest of China, 1731 m above sea level. The maximum water depth at the northeast is 13 m, with an average depth of 6 m. The water surface of the wetland is about 0.46 km2, while the floating aquatic plants cover 0.32 km2 of the water area. The aquatic plants float in the water surface like 'floating blanket', with thickness up to 2 m. The climate is a subtropical monsoon climate, with an average annual temperature of 14°C. The average maximum temperature is 31°C and the minimum temperature is -3°C. The frost period lasts for 110 d. The muti-years average precipitation is 1740 mm and the mean annual sunshine duration is 2153 h. The lake basin of the wetland is mostly peat marsh soil. There are plenty varieties of aquatic plants in the wetland. The 'floating blanket' mainly consists of Hydrophytes and Phreatophytes, including Iris laevigata Group, Leersia hexandra Group, Menyaanthes trifolia Group, Schoenoplectus spp Group, Phragmites communis Group, Myriophyllum spicatum Group and so on.

- Team: Tsinghua University | Coastal Ecosystems and Global Change Ecology Group (GCE)
- PI: Dr. Guanghui Lin, 林光辉
Gaoqiao mangrove station locates in an estuary (21°31'N~21°34'N; 109°44'E~109°47'E; altitude 0~5 m) southwest of Guangdong province, China, which belongs to Zhanjiang Mangrove National Nature Reserve. Gaoqiao station stands for sub-tropical coastal mangrove ecosystem, with subtropical and oceanic monsoon climate. The mean annual temperature and precipitation were 23.2°C and 1417~1802 mm. The coldest month was January, with average temperature 15.5°C and the hottest month, July, with average temperature 28.9°C. Cumulative sunshine hours was about 1864~2160 hours.
In addition, this station is almost frost-free. Gaoqiao station has mangrove, salt marsh and coastal psammophytic vegetation, but the dominating species were Avicennia marina, Aegiceras corniculatum, Rhizophora stylosa, Kandelia obovata (formly as K. candel) and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza. The vegetation under the flux tower is mainly mangrove forest, which canopy height is about 3 m. The soil is muddy soil, with organic matter content of 1.04~6.01%, nitrogen content of 0.056~0.284%, and pH from 3.7 to 5.9.

- Team: Shanxi University | Taiyuan Urban Wetland Flux (TYUW)
- PI: Dr. Gang Dong, 董刚
The region belongs to the temperate continental monsoon climate. The long-term mean annual air temperature of the region is 9.3°C, with the highest monthly mean temperature in July (22.8 °C). The mean annual rainfall varies between 180 mm and 466.6 mm, with the frost-free period is around 170 days. Soil is alluvial river sand soil. The dominant species in this region are Phragmites australis and Typha orientalis.
The eddy covariance and micrometeorological measurements are conducted in a 5 m tower on an island in the Fenhe River. Fluxes of CO2 and H2O are measured with an open-path gas analyzer (IRGASON, Campbell Scientific, Inc., CSI, UT, USA). The soil CO2 efflux is measured with a soil CO2 flux system (LI-8150 Multiplexer, LI-COR, Inc., Lincoln, NE, USA), leaf photosynthesis is measured with a Portable Photosynthesis System (CIRAS-2, PP systems, USA), and community photosynthesis and respiration are measured with a Portable CO2 analyzer (LI-820, LI-COR, Inc., Lincoln, NE, USA).
- Team: Chinese Academy of Forestry
- PI: Dr. Xudong Zhang 张旭东
The Yueyang Reed Ecosystem is located in the riparian zone of the Yangtze River, with a distance from the Yueyang Poplar Plantation of ~2 km. It has an area of 140 ha and Phragmites Adans is the dominant species. This site has been managed as a reed plantation for more than 10 years, which can represent the original ecosystem of this region. This site was established in 2014, and the CO2, CH4, water vapor and energy was observed at present.

- Team: Tsinghua University | Coastal Ecosystems and Global Change Ecology Group (GCE); ); Xiamen University | Coastal Ecology and Remote Sensing (CERS)
- PI: Dr. Guanghui Lin and Xudong Zhu
The Yunxiao station is located in the Zhangjiang Estuary Mangrove National Nature Reserve, south of Fujian Province and about 95 km away from Xiamen (117°21'-117°30' E; 23°53'-23°57' N. The Yunxiao station stands for sub-tropical coastal mangrove ecosystem, with a subtropical and oceanic monsoon climate. The mean annual evapotranspiration and precipitation were 1718.4 mm and 1714.5 mm, respectively, most of which occurs from April to September.
The annual mean temperature was 21.2°C, with the lowest of 0.2°C in January, and the highest of 38.1°C in August. Cumulative sunshine hours were about 2125.1 hours and relative humidity is about 79%. The Yunxiao station has mangrove, salt marsh and coastal psammophytic vegetation, but the dominating species are Kandelia obovata, Avicennia marina, Aegiceras corniculatumand Bruguiera gymnorrhiza, and invasive species Spartina alterniflora. The vegetation under the flux tower is mainly mangrove forest, which its canopy height is about 3~5 m. The soil is alluvial soil, with an organic matter content of 0.674~2.448%, nitrogen content of 0.069~0.208% and pH from 4.8 to 7.0.

- Team: Beijing Forestry University
- PI: Dr. Tianshan Zha, Dr. Peng Liu, Dr. Xin Jia

- Team: Institute of atmospheric physcis, Chinese Academy of Sciencesp
Beihai wetland observation site (25°07'N, 98°33'E) is located in the central mountainous area of Tengchong County, in the west part of Yunnan Province, China. This site was established in June 2015. The area has the low cutting landform of middle-mountain in the west slope of Gaoligong Mountain. It is the only natural plateau marsh wetland originated from a volcano created quake lake in the southwest of China, 1731 m above sea level. The maximum water depth at the northeast is 13 m, with an average depth of 6 m. The water surface of the wetland is about 0.46 km2, while the floating aquatic plants cover 0.32 km2 of the water area. The aquatic plants float in the water surface like 'floating blanket', with thickness up to 2 m. The climate is a subtropical monsoon climate, with an average annual temperature of 14°C. The average maximum temperature is 31°C and the minimum temperature is -3°C. The frost period lasts for 110 d. The muti-years average precipitation is 1740 mm and the mean annual sunshine duration is 2153 h. The lake basin of the wetland is mostly peat marsh soil. There are plenty varieties of aquatic plants in the wetland. The 'floating blanket' mainly consists of Hydrophytes and Phreatophytes, including Iris laevigata Group, Leersia hexandra Group, Menyaanthes trifolia Group, Schoenoplectus spp Group, Phragmites communis Group, Myriophyllum spicatum Group and so on.



